Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
AsteroidOS review - the future of Android Wear?
Published onDecember 24, 2016

With Android Wear 2.0 being delayed until the next year, and seemingly no new smartwatches planned from OEMs like LG, Motorola, and HUAWEI, things in the Android Wear universe has come to a standstill. If you can’t wait for the Android Wear 2.0 update, or are just looking to breathe some life into your smartwatch, you might want to give something new a try. Currently compatible with a limited number of devices, including what was the first Android Wear smartwatch to be launched, the LG G Watch, here is a quick look at AsteroidOS!

AsteroidOS has been created by Florent Revest, a French computer science student, and is a completely standalone linux-based wearable OS that is not based on Android Wear in any shape or form. It is also entirely open-source, which will allow other developers and manufacturers to freely modify it as they see fit.
Before diving into the review, something to keep in mind is that AsteroidOS is still in the alpha stages of development, so understandably, not everything will work perfectly. You will notice a lot bugs and freezes, but it does run well enough for you to get an idea of what this new take on the wearable operating system has to offer.
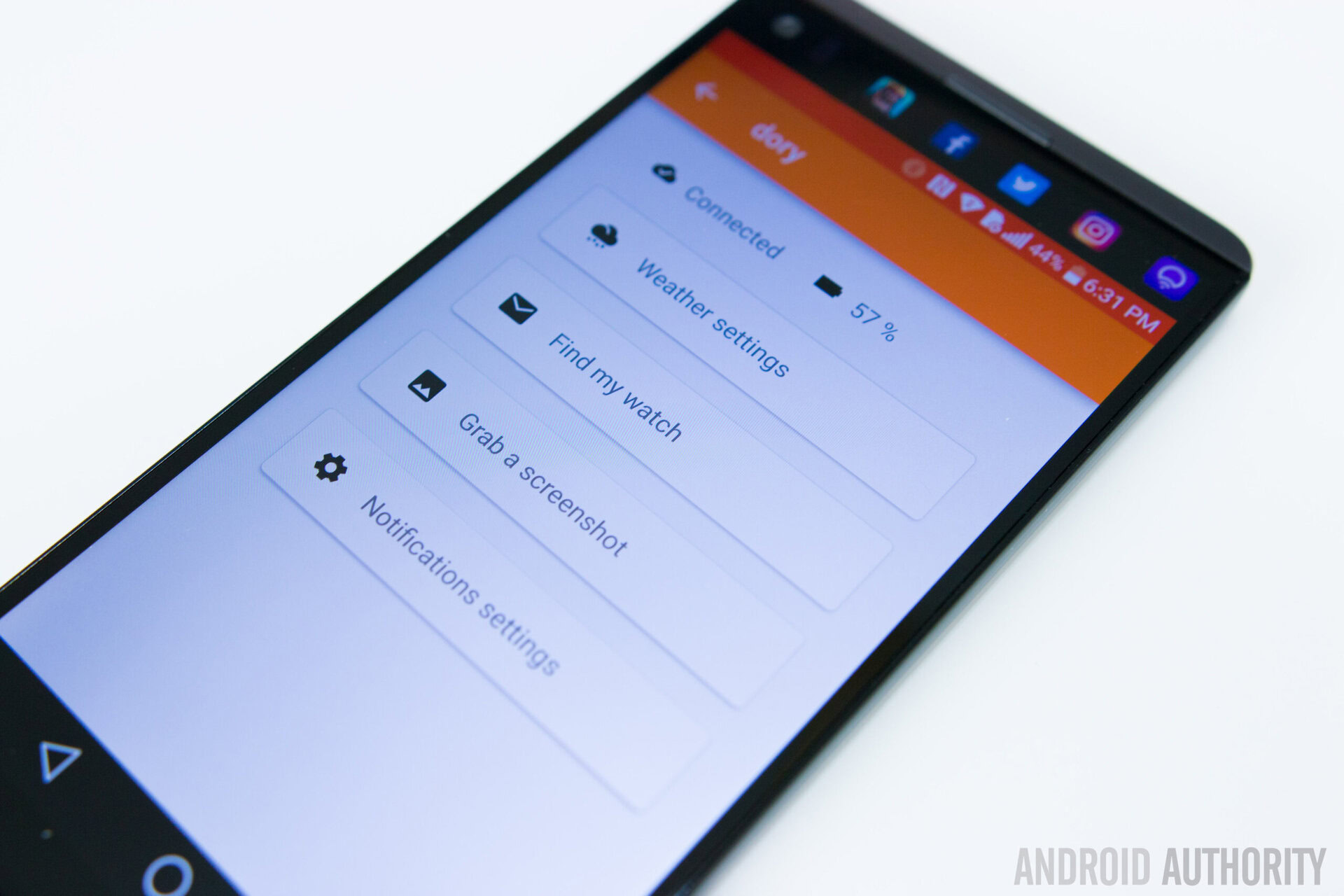
There is an app you can download from the AsteroidOS website, that will allow you to manage certain functions and pair it to your smartphone for notifications. So far, the smartwatches that AsteroidOS can be ported to include the LG G Watch, the LG Watch Urbane, the Sony Smartwatch 3, and the ASUS Zenwatch 2, but that list should continue to grow.
Bluetooth pairing works only with the LG G Watch however, and even then, it can be quite finicky. The connection isn’t always stable, and notifications tend to disappear after a few seconds, with the watch going back to saying that you have no new notifications. So far, there isn’t a way to interact with, or even read, notifications either.

When the watch is connected to the phone, you have several options within the app itself. You can change the weather to the city of your choice, locate your watch, take a screenshot, and tinker with the notification settings. The weather settings and the find my watch options are currently the only features that work for now. The app also tells you the remaining battery life of your smartwatch, but it isn’t accurate at the moment, so you are better off checking the device’s battery life on the watch itself.
Since it is touch based, all the navigation is done via swipes. If you swipe down on the display, you will get access to some quick shortcuts for screen brightness, Bluetooth, and enabling or disabling vibration, and you can also see the remaining battery life here. If you tap on the lock icon, it will put the watch to sleep, and a double tap on the display will wake it up.
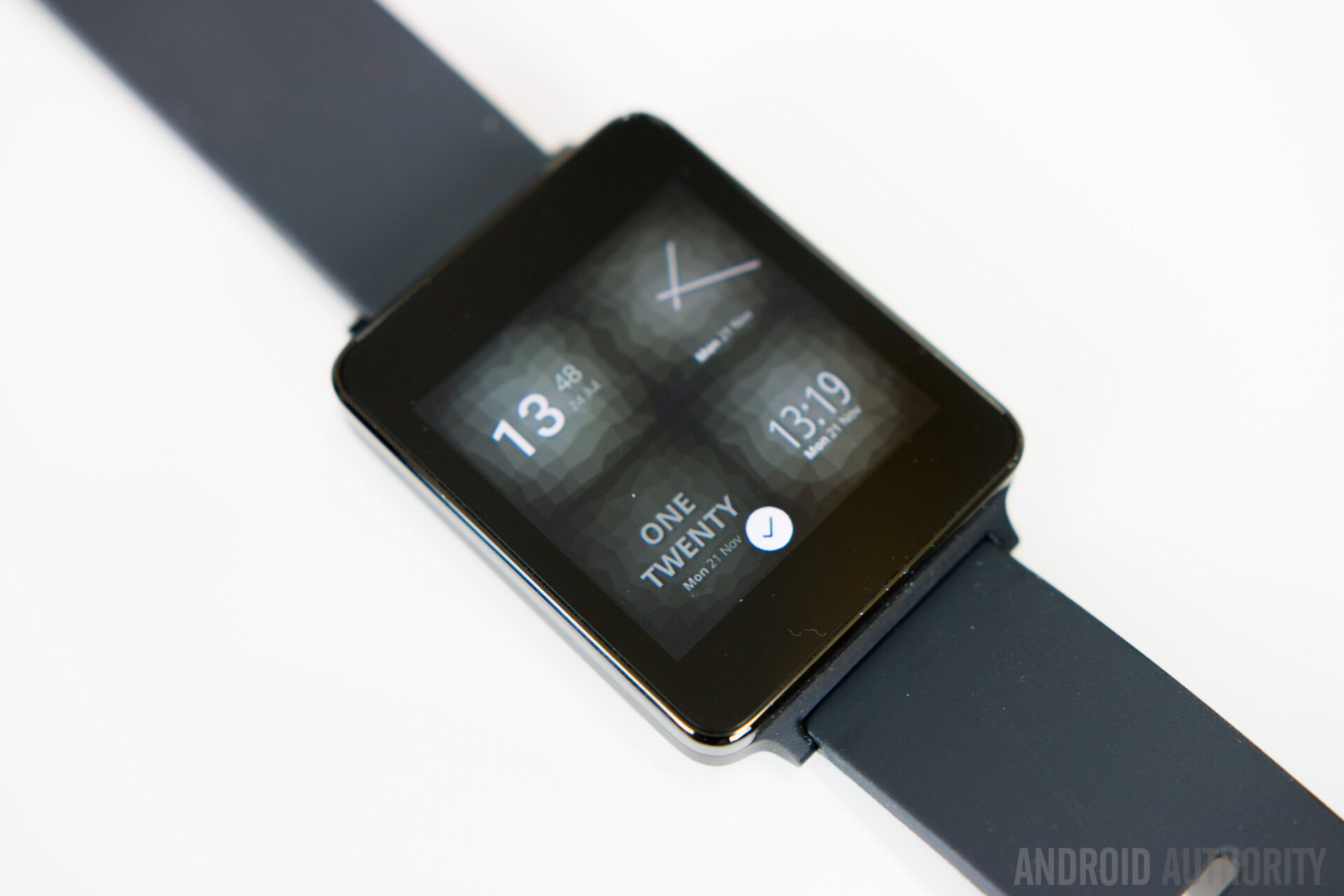

Swiping to the left will show you your notifications, assuming that notifications work properly. Swiping right works like a back key, unless you are already on the main home screen , in which case a swipe to the right will take you to the Recent Apps screen. Here, you can quickly jump between apps, and easily close these apps with a long press on them, and tapping the x that appears.
No third party apps are available at the moment, but there are a few basic applications that are pre-installed that you can access by swiping up on the screen. These include a calendar, calculator, alarm clock, timer, stopwatch, a music player, and a weather application. All the apps are simple and minimalistic, with white text and graphics, and colorful backgrounds.
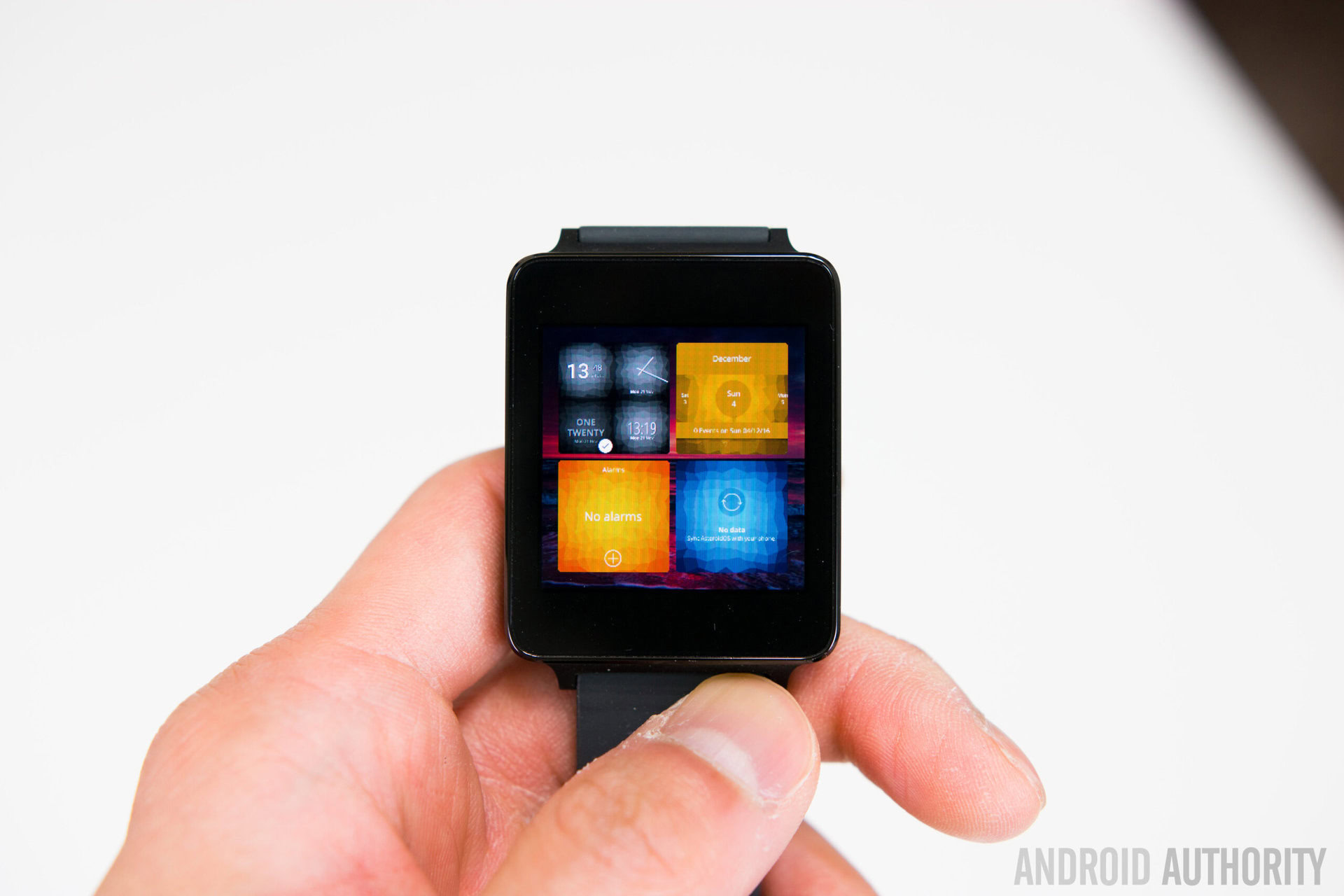

You can also access all the watch settings here, which has all the basic functions that you would expect, like the time, date, language, Bluetooth, screen brightness, and the options to power off or reboot the watch. There are also some customization options here for wallpapers and watch faces, and it comes pre-installed with a surprisingly decent amount of them, given that it is such an early build.
So, there you have it for this quick look at the AsteroidOS! If you are looking to install this new wearable operating system, you can find all the information you need here. Keep in mind though that the installation process isn’t easy, and some amount of technical prowess is definitely recommended.
Another thing to consider is that this isn’t daily driver material just yet. Instead, what you will get instead is a fair idea of what the experience is like, and what to expect going forward. It doesn’t overwrite Android Wear either, so you can easily go back to the regular OS by simply rebooting the watch. Asteroid OS is a wearable operating system that looks like it has a lot of potential, and is definitely worth keeping an eye on to see where it can go from.