Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
Gmail IMAP settings: What they mean and how to set them up
Published onAugust 9, 2023
When you take a peek into Gmail’s settings, everything is pretty straightforward until you notice the Gmail IMAP settings and wonder what they’re used for. This article will explain the Gmail IMAP settings and how to configure them.
QUICK ANSWER
You can use Gmail IMAP when you want to download your Gmail emails to an email client on your computer, such as Outlook. IMAP will download the messages and sync your changes back to the Gmail servers so everything stays the same.
A guide to Gmail IMAP settings

Not everybody likes to use the online version of Gmail. Some still prefer the old-fashioned way of using email clients such as Microsoft Outlook, iOS Mail, or macOS Mail. Some may even like using the outdated and now obsolete Mozilla Thunderbird. Others have employers who force them to use it.
If you find yourself in the email client camp willingly or unwillingly, then IMAP is there to make your life easier. It’s very easy to set up, as you’ll see below.
How to set up Gmail IMAP
Go to Gmail’s Forwarding and POP/IMAP page on the desktop, scroll down till you reach the IMAP settings section, and select Enable IMAP.
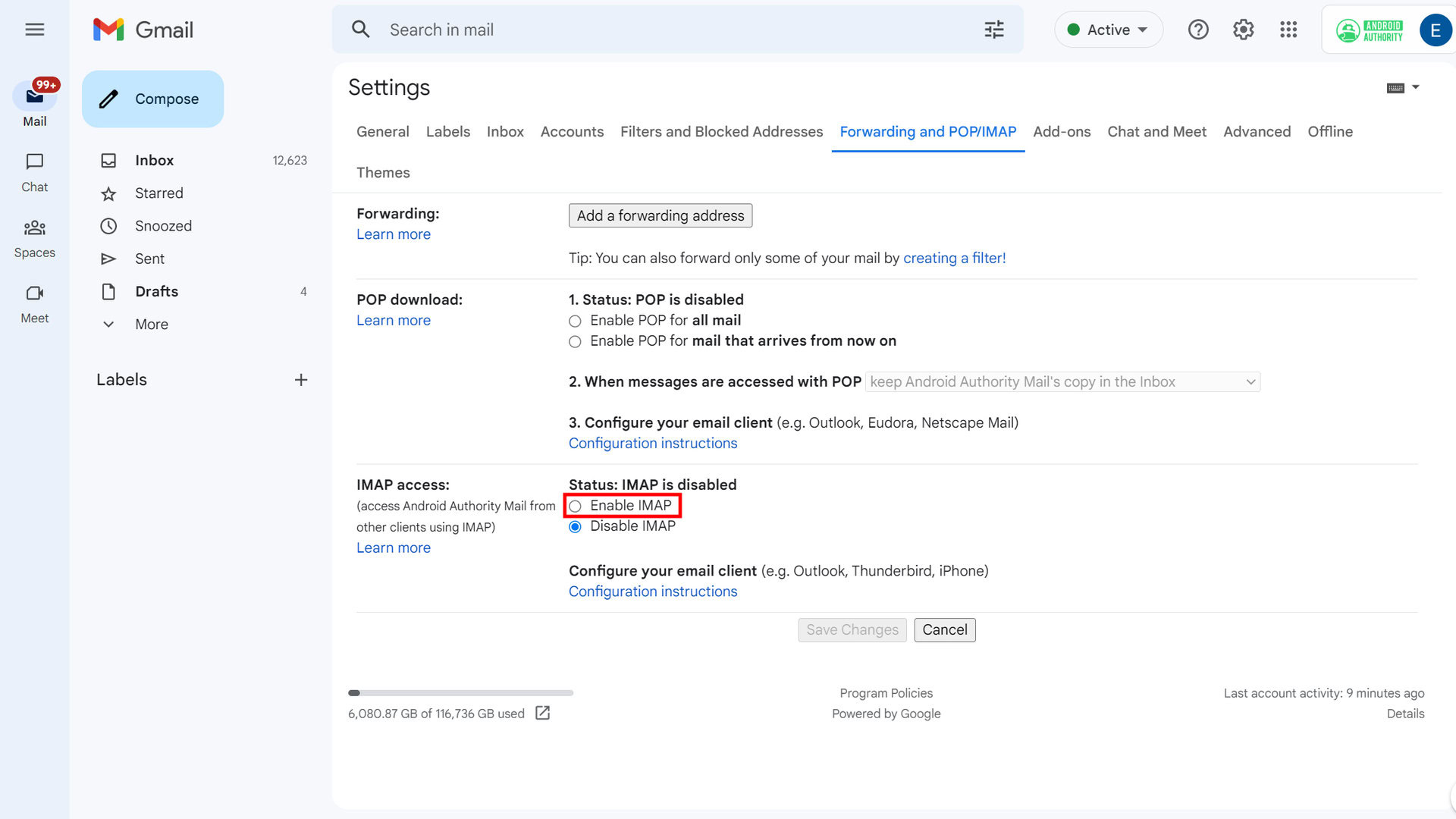
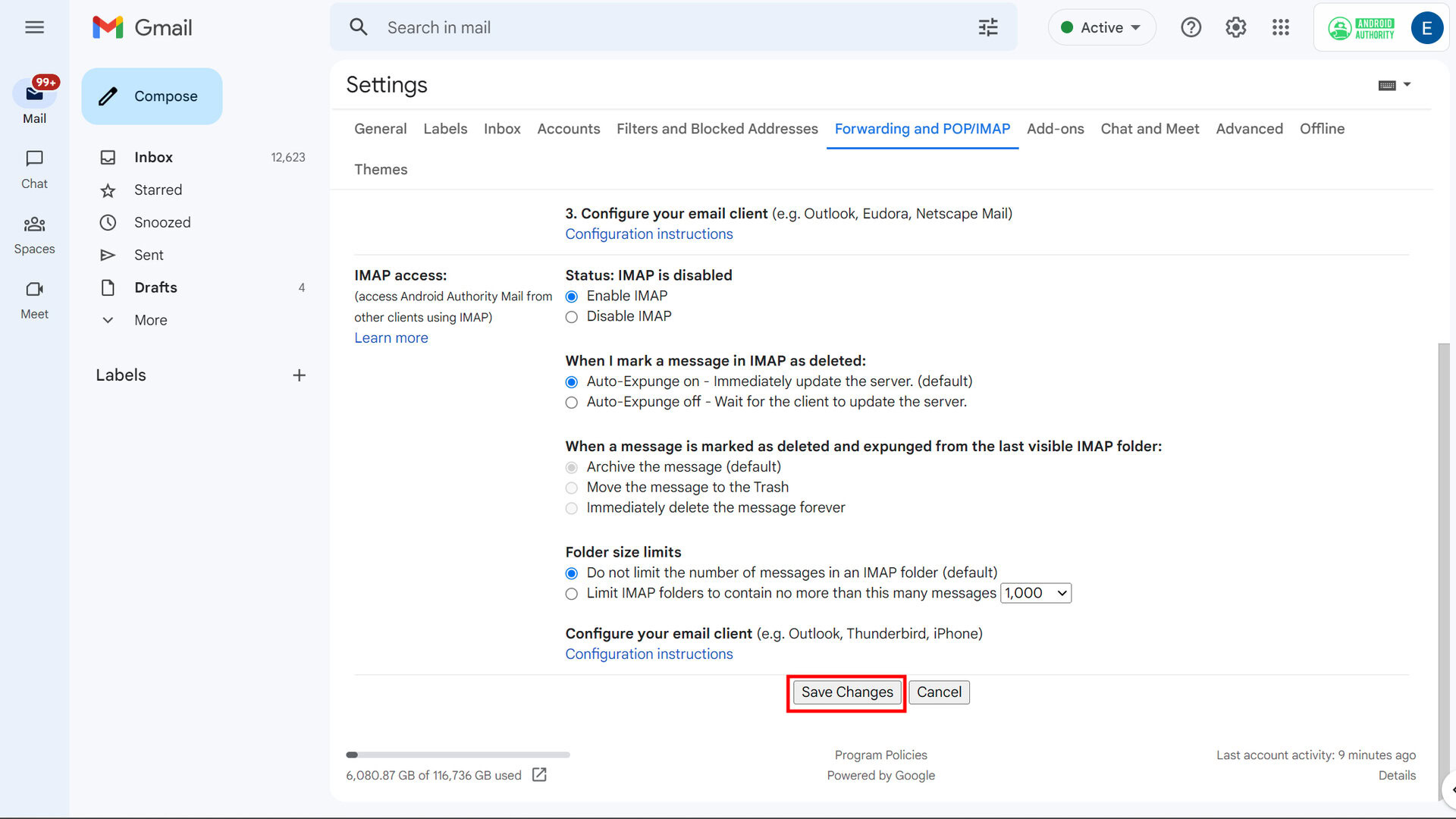
When you’ve selected Enable IMAP, new options appear but don’t change any of them. Just select Save Changes.
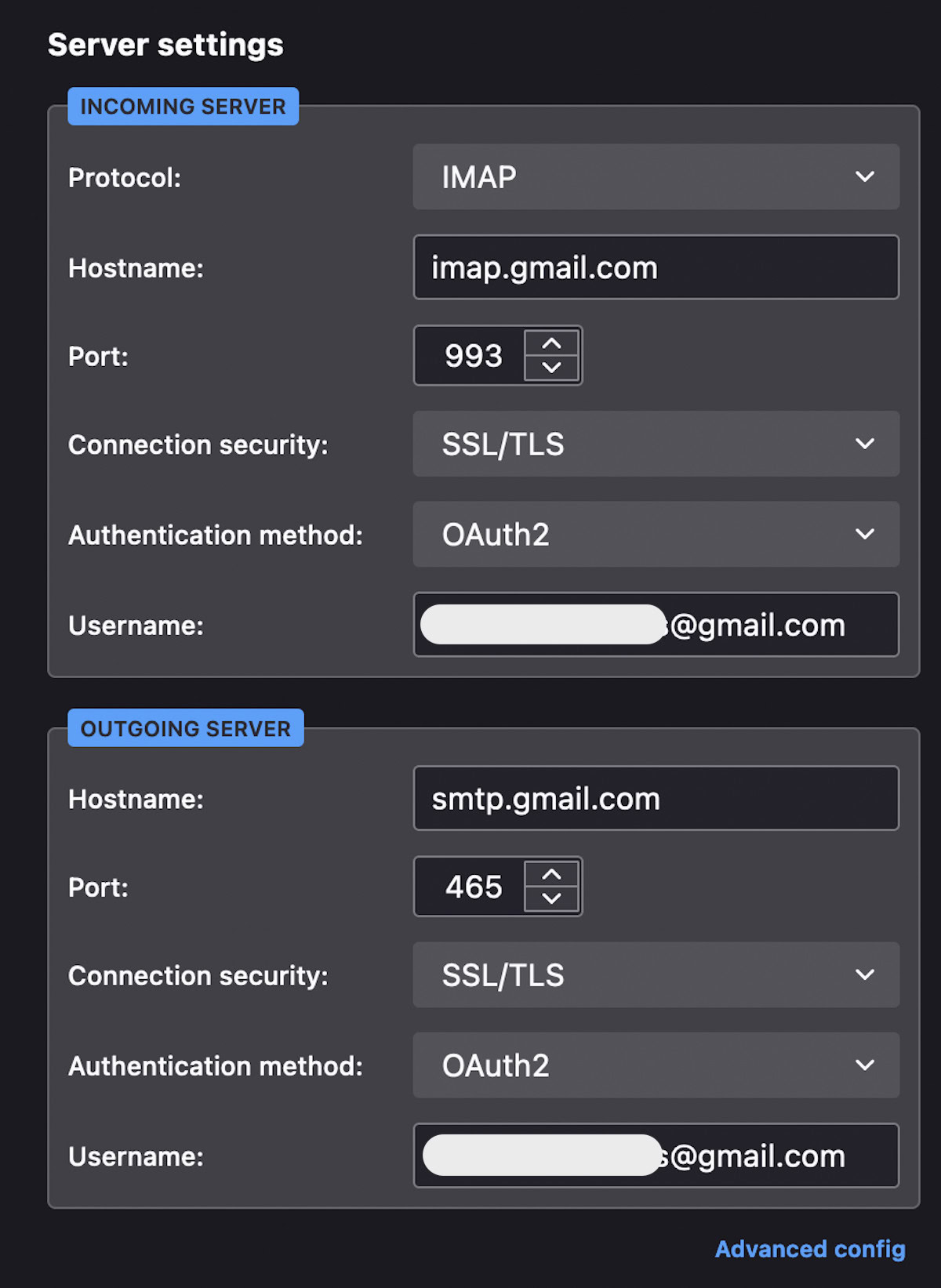
To access your email through your email client, use these configurations.
| Incoming Mail (IMAP) Server | imap.gmail.com Requires SSL: Yes Port: 993 |
| Outgoing Mail (SMTP) Server | smtp.gmail.com Requires SSL: Yes Requires TLS: Yes (if available) Requires Authentication: Yes Port for SSL: 465 Port for TLS/START TLS: 587 |
| Full Name or Display Name | Your name |
| Account Name, User name, or Email address | Your full email address |
| Password | Your password |
Not all the information may be required. Thunderbird, for example, doesn’t ask for your name.
The screenshot below shows what the email client configuration screen should look like once you fill in the correct Gmail IMAP options.
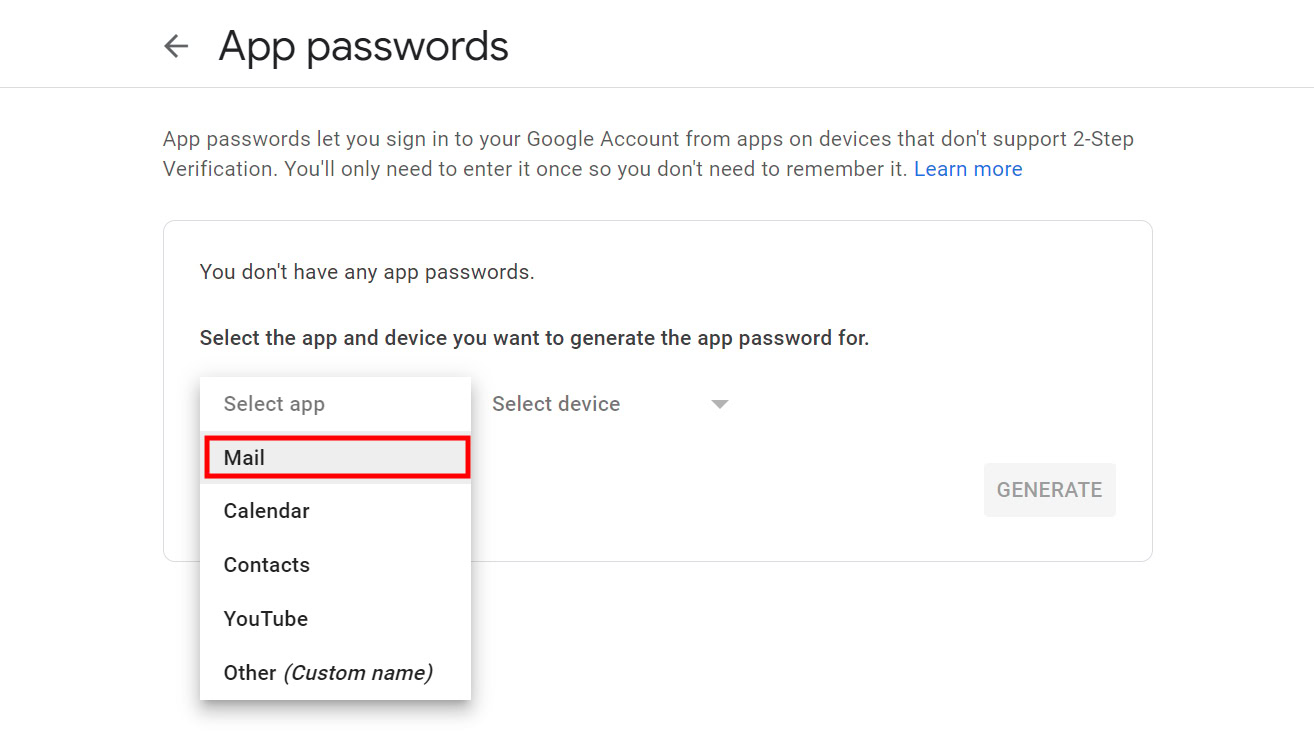
It should also be noted that if you have two-factor authentication enabled on your email account, giving the email client your password will not work. In that case, you need to generate an application-specific password in the Security section of your Google account.
FAQs
The difference is where your emails are stored. IMAP messages are downloaded to your local email client and synchronized with the email server (in this case, Gmail). So if you send a message with Outlook, that message will get uploaded to Gmail’s servers to sit in your Sent folder. On the other hand, POP only downloads copies of your emails to your local email client. It does not send new messages back to the email server.
IMAP retrieves messages from your email server and downloads them to you. SMTP, meanwhile, is for sending emails from the sender (you) to another email server.
So IMAP downloads emails locally, and SMTP sends emails from another email client. In turn, POP is for receiving emails from another email client or account. It works in tandem with SMTP to both receive and send emails with a different email client.