Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
How does AirDrop work? Our experts have answers
Published onAugust 25, 2023

Most of us know and use Apple’s AirDrop feature to wirelessly share photos and other material with nearby Mac and iOS devices. But how does it work? In this article, we’ll dive into the details of AirDrop’s underlying technology, which might help you understand its advantages and limitations.
QUICK ANSWER
AirDrop transfers files using TLS encryption over a direct Bluetooth-enabled peer-to-peer Wi-Fi connection. The Wi-Fi radios of the source and target devices communicate directly, bypassing an internet connection except in specific scenarios allowed by iOS 17.
KEY SECTIONS
What is AirDrop?
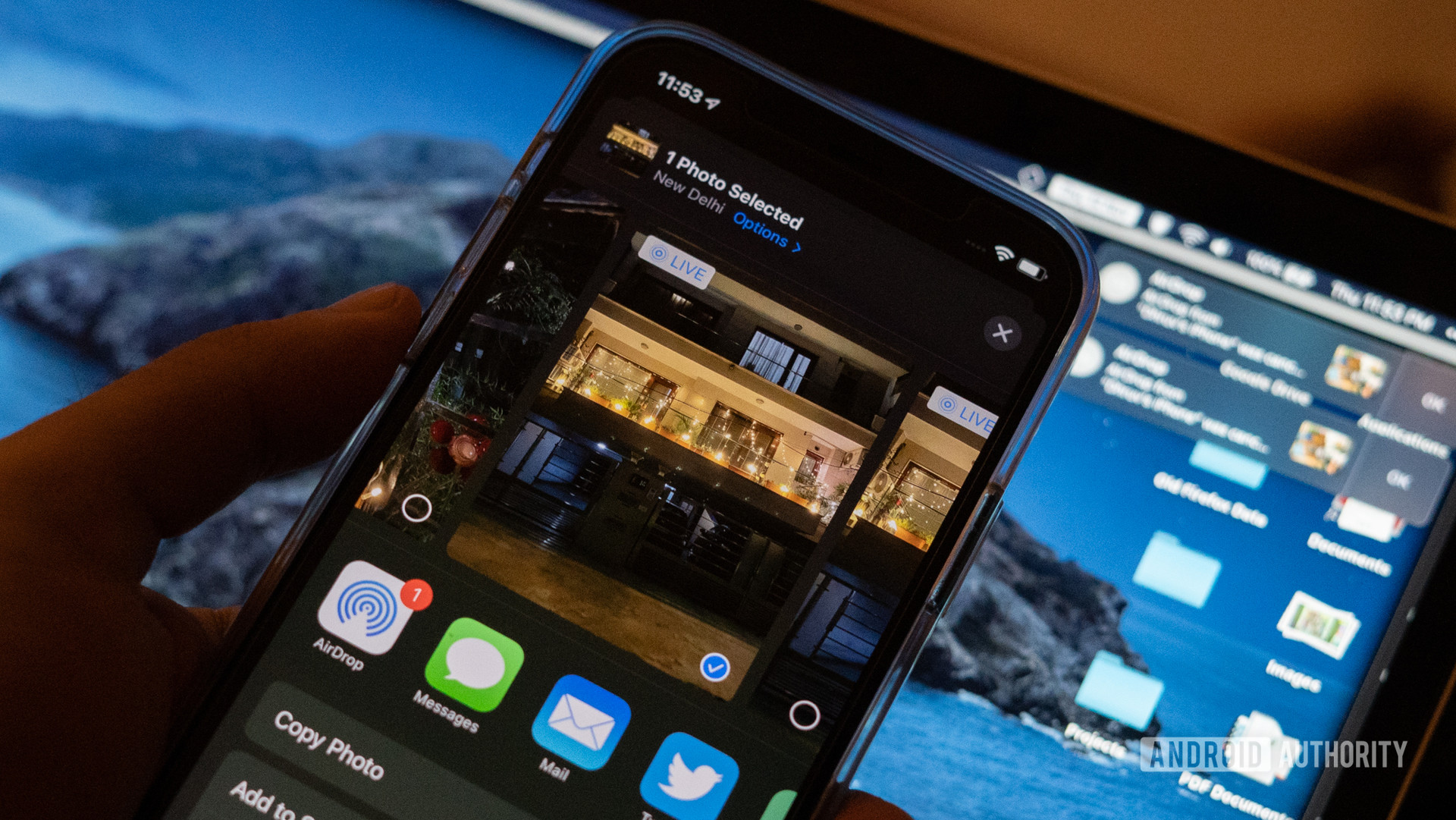
AirDrop is a feature native to iOS, iPadOS, and macOS intended to simplify the process of sharing content with people nearby. Users can wirelessly send and receive photos, links, videos, notes, playlists, locations, and more, as long as both people have Apple devices. There’s no apparent limit on the size of files AirDrop can transfer.
Android has its own equivalent in Nearby Share, but the two work somewhat differently. For instance, AirDrop is subject to certain iOS restrictions, such as the inability to share music or videos from native apps.
See also: How to transfer photos between an iPhone and Android
AirDrop is supported on Apple devices running at least iOS 7 or macOS 10.10 (Yosemite). Technically speaking it existed on Macs prior to Yosemite, but it used a different protocol, limiting it to Mac-to-Mac transfers.
Sometimes the technology has been utilized in unsavory ways. Cases have been reported in which people with AirDrop privacy set to “Everyone” received unwanted files from nearby strangers; the phenomenon has been dubbed cyber-flashing. In June 2022, for example, a man on a Southwest flight reportedly AirDropped a sexually explicit photo to all passengers aboard, leading to police waiting to escort him off the plane on landing. Because of these events, Apple quietly started limiting the “Everyone” mode to only 10 minutes as of iOS 16.2.
AirDrop has even been instrumental in protests. For example, Chinese users turned to AirDrop to distribute posters and slogans following the 2022 Beijing Sitong Bridge protest. Apple reportedly limited AirDrop functions in China just weeks before subsequent COVID-19 demonstrations.
How does AirDrop work?
Communication takes place over Apple Wireless Direct Link using generated link-local IPv6 addresses instead of a Wi-Fi chip’s fixed MAC address. In plain English, that means the device wanting to send an AirDrop emits a Bluetooth signal to detect devices within the vicinity. It also creates an iCloud identity based on the email addresses and phone numbers associated with a user’s Apple ID.
Once a device with AirDrop turned on is found and selected, a peer-to-peer Wi-Fi connection is created. So while you need to have Wi-Fi turned on on both devices, they don’t need to rely on a nearby router. The underlying software AirDrop uses is Bonjour, Apple’s built-in service discovery tool for macOS and iOS.
When using AirDrop, the sender selects who they want to share with. The sending device initiates an encrypted (TLS) connection with the receiving device, which exchanges iCloud identities. The identity is verified against each user’s Contacts app. Then the receiving user is asked to accept the incoming transfer from the identified person or device. This process is repeated for each device if multiple recipients have been selected.
In the Everyone mode, the same process is used, but if a match in Contacts isn’t found, the receiving devices are shown in the AirDrop send sheet with a silhouette and a device’s name. Although strangers don’t see your identity, they can still send you AirDrops should you decide to receive them.
Two key additions have been made in iOS 17. The first is proximity sharing, which allows devices to initiate an AirDrop simply by bringing them inches apart. Sharing options will pop up, but once those are selected, transfer will begin immediately — permission is assumed, and you don’t even need to have AirDrop enabled. This can be toggled via Settings > General > AirDrop > Bringing Devices Together if you’re concerned.
Next up is internet-based transfers. While AirDrops must always start locally, if someone has to leave, they can continue via iCloud — no more waiting several minutes while a large video copies. All people involved must be running iOS 17 or later and be signed into iCloud.
FAQs
If AirDrop isn’t working on your iPhone, try these nine troubleshooting tips.
A crypto AirDrop uses AirDrop to deliver tokens to the wallets of current cryptocurrency traders, either for free or in exchange for a small promotional service. It’s usually a marketing method to spread awareness or increase ownership of the currency startup.
AirDrop works on Macs running macOS X Lion (10.7) or later. As we’ve noted, though, only macOS 10.10 (Yosemite) or later supports exchanges with iPhones and iPads.