Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
How to secure your home Wi-Fi network
Published onMarch 8, 2023
Wi-Fi is the backbone of home connectivity. Be it your laptop, smartphone, or the dozens of smart home devices strewn across your home, they are all connected to your Wi-Fi router to enable a world of experiences. But going online also means leaving yourself vulnerable to a range of threats like viruses, hacking, or network intrusion. Learning how to secure your home Wi-Fi network is critical to ensuring a safe online experience.
QUICK ANSWER
The best way to secure your Wi-Fi network is to set a unique SSID or broadcast name and to use a complex alphanumeric password ranging between eight to twelve characters. You should also change the default username and password for your router's administration page.
BEST WAYS TO SECURE YOUR WI-FI NETWORK
Change the default SSID and password
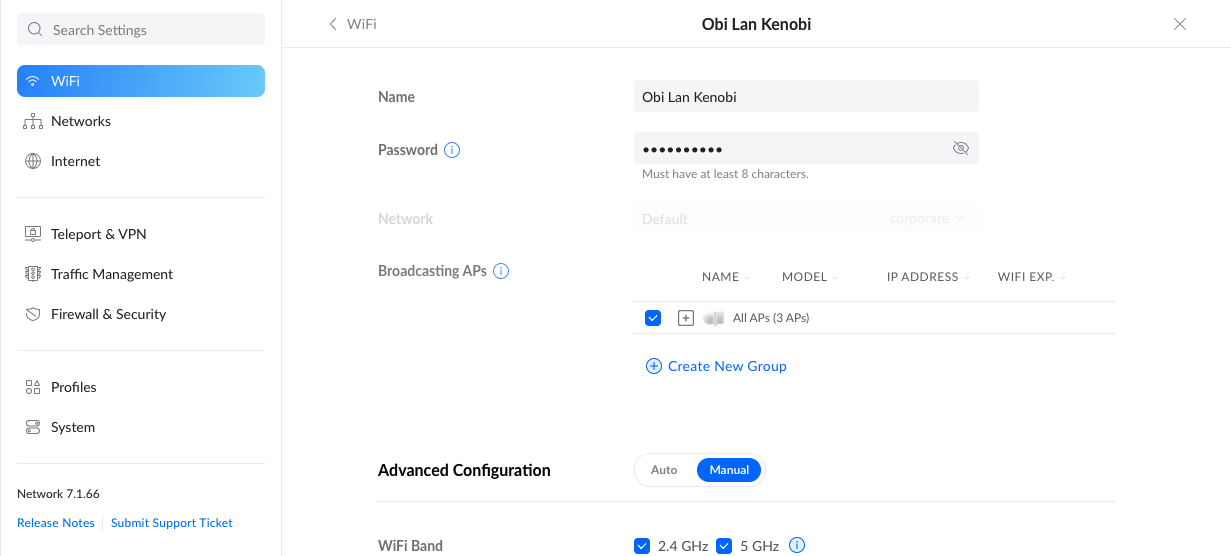
Most routers ship with a default name that is broadcast as the router’s SSID. This SSID, also known as Wi-Fi name, can give away what brand of router you are using. Router manufacturers often use insecure passwords, or might even reuse passwords across devices, and as such, changing the SSID and Wi-Fi password is the first thing you should do while setting up your router.
The exact procedure for changing the Wi-Fi password can vary depending on the specific model you use, but look for the Wi-Fi or WLAN setting under your router’s admin page. This page can usually be accessed by heading over to 192.168.1.1 via your browser. From there, set any recognizable name as your SSID. Feel free to get creative with it.
As for the password, it is highly recommended that you choose an alphanumeric combination with at least 8—12 characters. For added complexity, you can even include different cases and special characters. The harder it is to guess, the more secure is your Wi-Fi network. If your password gets too complex to remember, we recommend using a password manager app alongside.
Change the router username and password
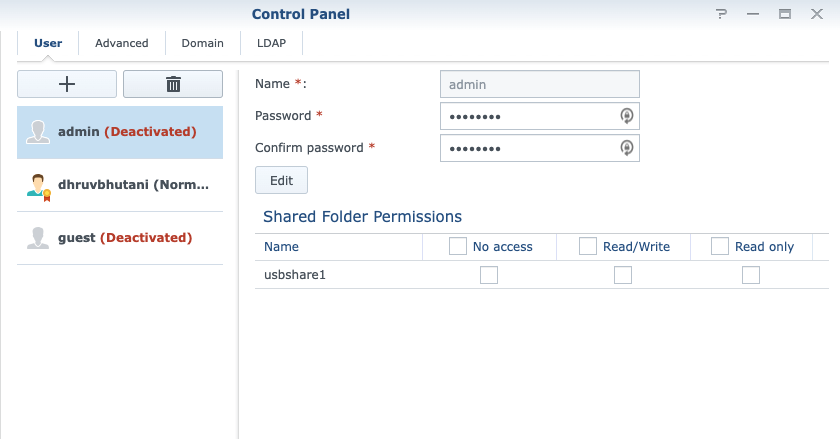
While a complex Wi-Fi password will do the lion’s share of keeping your home network secure, it can still be breached if someone manages to brute force or guess the password. Blocking off access to your router’s administration page is the next step to follow. Most routers will have admin as the default username. This is, obviously, very easy to guess.
Head to user settings under your router’s settings page and change the default user’s name to a unique username. Follow the same advice as for Wi-Fi passwords to change the password for the admin account. Taking it a step further, it is always a good idea to disable the default admin account as well, as it usually has access to all the router settings.
Enable encryption
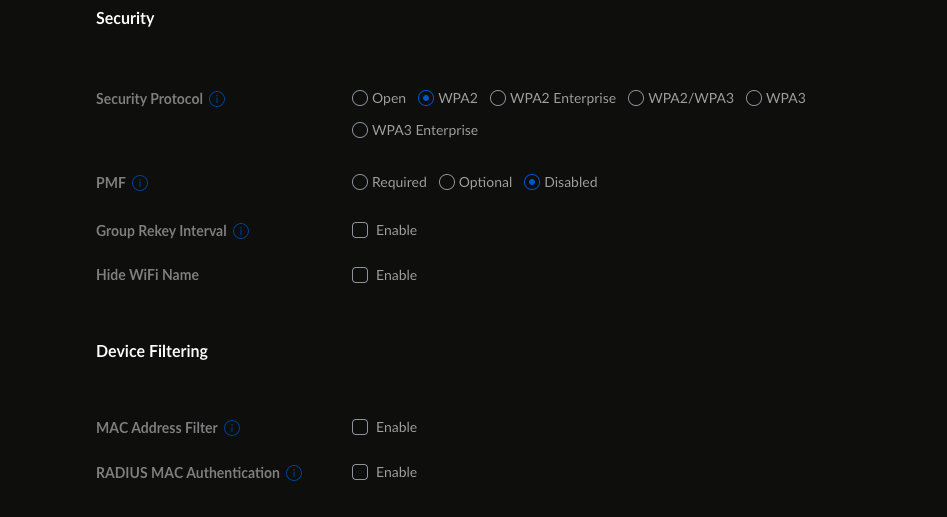
Encryption makes sure that the traffic or data moving between your phone or laptop and the Wi-Fi router cannot be intercepted. This interception technique is called packet sniffing. Most modern routers will automatically select WPA2 encryption as the default, however, it is a good idea to check that you are on the latest standards. Head on over to the Wi-Fi page under your router’s admin settings and make sure that it is set to WPA2 or WPA3. Note, that WPA and WEP are insecure protocols and have long been compromised. In the unlikely case that your router does not support any higher standard than WPA or WEP, it might be a good idea to upgrade to a new one.
Enable the firewall
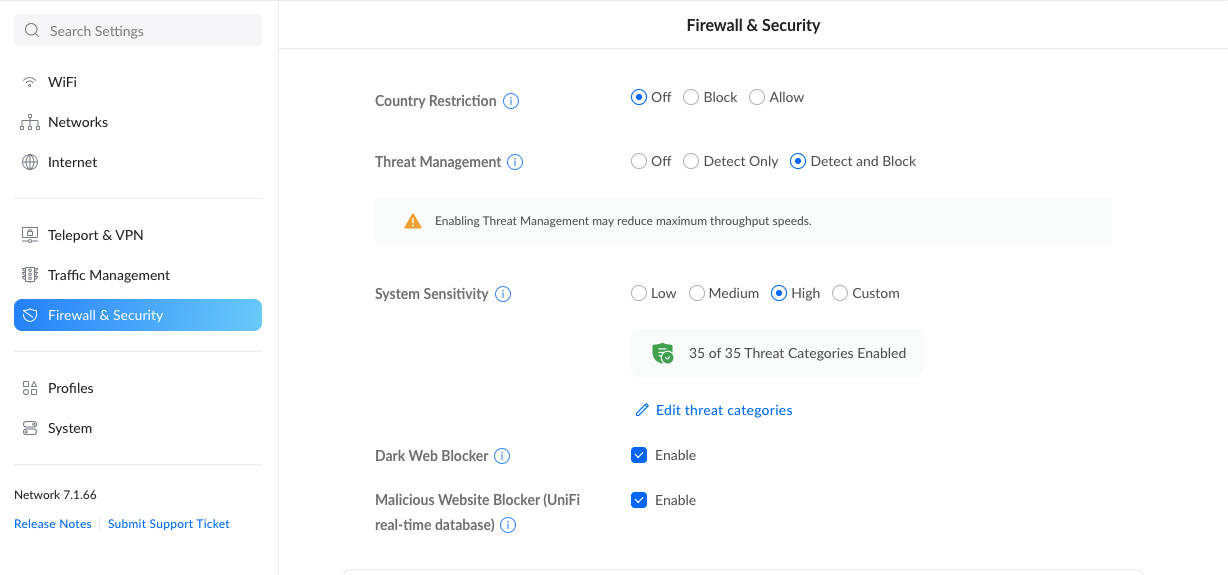
A firewall, as the name suggests, acts as a filter between incoming and outgoing network traffic. It acts as a barrier against untrustworthy internet traffic in the form of attacks or hacking attempts by comparing your incoming internet traffic against a set of security rules and protocols. If the firewall thinks that an unauthorized computer is trying to access your network, it can alert you or block the threat automatically.
Most routers ship with at least a rudimentary firewall built-in. This is usually tucked away under advanced settings. On entry-level routers, a firewall can impact the overall speed of the network due to the added task of processing the traffic, but enabling it is well worth the minor hit to speed.
Turn off remote management and UPNP
Mid-range and premium routers often ship with a remote management utility built-in. These apps can help you keep a tab on your router’s current status, speed, and access point-related information from a remote location. Some might even let you use the router for downloading files. Unfortunately, the services are rarely kept secure and up-to-date over the years. It’s a good idea to disable them for additional security. In case you do want to access your router remotely, a reverse proxy service like no-IP or DynDNS can do the same but with much more peace of mind.
Similarly, UPNP was created to enable easy discovery of other devices on your network. However, it is an antiquated and insecure protocol that can be hacked into. Disabling it in Wi-Fi settings is generally a good idea.
Keep your router’s software updated
Your router runs on its own software (often called firmware). There is a possibility that this software is found to have some flaws or security vulnerabilities. In such instances, the router manufacturer will issue a firmware update that will fix the vulnerability.
Your router should ideally keep itself auto-updated. However, it is good practice to routinely check for an update and ensure that you are on the latest possible firmware. This habit will minimize your exposure to any vulnerability that compromises the security of your network.
Some routers will also let you manually update through a local firmware file that can be downloaded from the manufacturer’s website. However, we do not recommend most users attempt a manual firmware upgrade.
If you do not see a firmware update section in your router’s settings, you may not have the requisite permissions. This can happen in instances where the router was supplied by your broadband provider. If you spot that the firmware version is several years old, it is worth contacting your broadband provider to ask if there is a firmware update available. Chances are that they will upgrade your router hardware if it is too old (at a cost sometimes, so please check with your broadband provider about any charges).
Create a guest network for temporary connections
You are bound to have guests come over to your house, and some may expect to use your Wi-Fi connection. In situations like these, it may be impolite to decline their request. At the same time, granting access to your primary Wi-Fi to devices you do not completely trust is also a big security issue. Doing so opens up access to other devices connected to your home network, such as smart home devices, printers, NAS devices, and shared folders on the network.
In such situations, you can create a guest network for these temporary connections to your Wi-Fi. This way, your guests will have access to the internet without having access to the other devices on your primary network. You can also share the password of the guest network without revealing the password of your primary network. And once the guests leave, you can change the guest network password or disable the guest network entirely — all without affecting your primary network and devices connected to it.
Most routers will ship with the ability to create a guest network. The feature usually resides under the WLAN/Wireless Network settings page. There, you can enable the guest network, and give it a name and password. Some routers will also present a setting for enabling/disabling access to your local network, with the default being off. And some routers will allow you to set a timer for the guest network, switching off the guest network at the end of it.
If you want to double down on security, you can enable the guest network and then hide your primary network’s SSID. This way, your primary network will not be visible to people scanning for it, and they’ll need to know the exact SSID as well as the password to connect to your primary network. Guests will see your guest network, which you can toggle off once you no longer need to share access.
FAQs
A Wi-Fi security key is the password that is used to log into your Wi-Fi network. It is recommended that you use a complex alphanumeric code as the security key.
Passpoint or Hotspot 2.0, as it is often called, is a solution for accessing a range of commercial Wi-Fi hotspots. It passes your credentials across all passpoint-compatible hotspots ensuring that you no longer need to select the access point or enter a password.
The quickest way to kick someone off of your Wi-Fi is to change your Wi-Fi password, although you can take it one step further and block their MAC address, too.