Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
What does "E" mean on my phone?
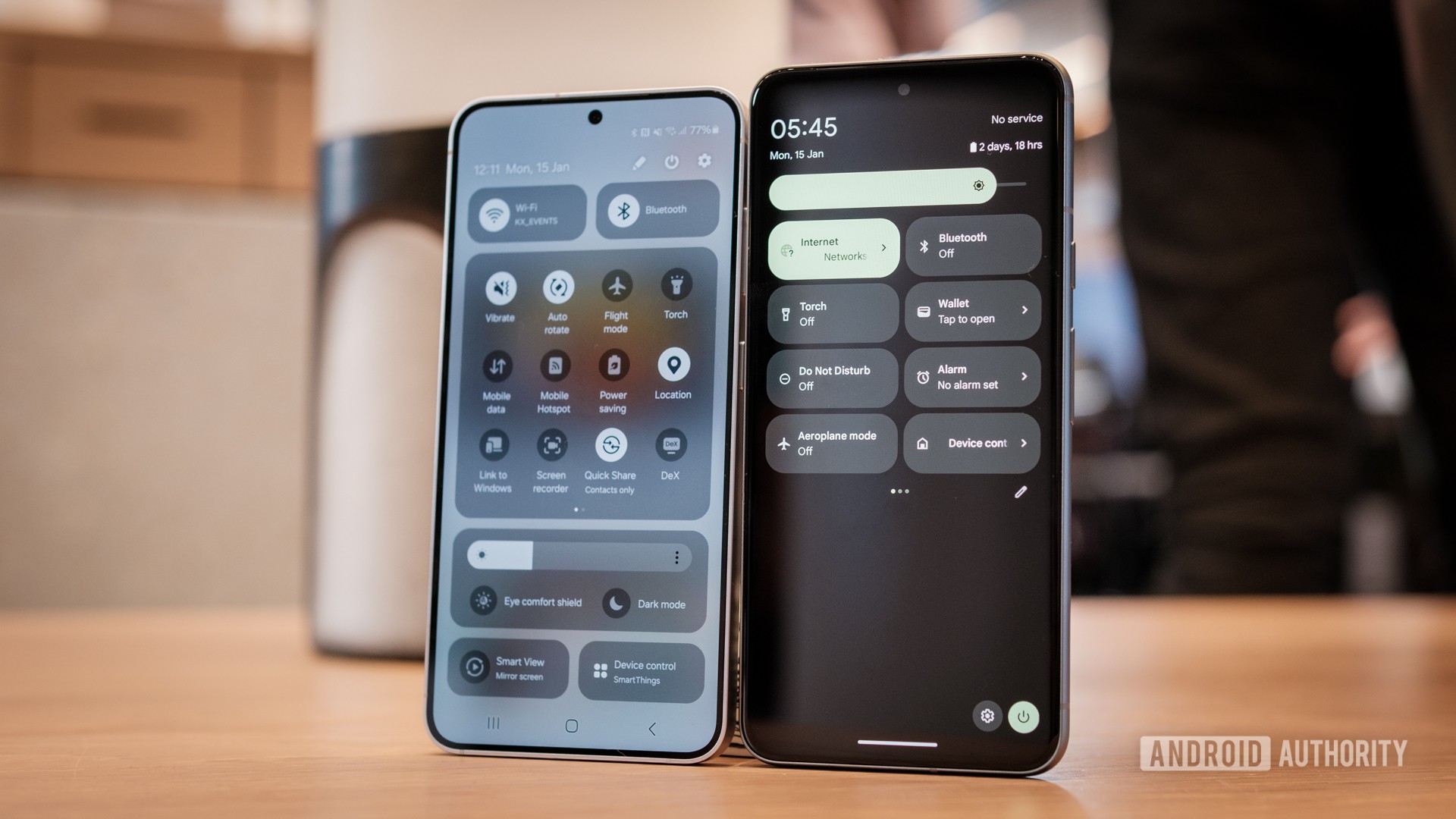

Whether you own an Android phone or an iPhone, you might be surprised to spot an “E” icon appearing at the top of the status bar on your phone screen on occasion instead of 5G or LTE. Coincidentally, your phone’s data connection also slows down to a crawl whenever that happens. That’s no coincidence – here’s what the “E” symbol means on your phone and how to make it go away.
QUICK ANSWER
The E symbol on your phone indicates that your phone is connected to your carrier's legacy 2G EDGE network. This usually happens when the device is on the verge of losing network connectivity as EDGE or 2G is the oldest and least advanced cellular technology still in use today. The internet experience on a 2G network is not ideal, with crawling data speeds that may not prove sufficient to even send a single chat message.
JUMP TO KEY SECTIONS
What does “E” mean on my phone?
The “E” on your phone’s status bar refers to EDGE, which is short for Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution. EDGE is the evolved form of GPRS, but both often get put into the same bucket as what most people commonly recognize as 2G. As a refresher, GPRS was the first step of data service on a mobile network and EDGE was a step up in speed and bandwidth.
E stands for EDGE or legacy 2G networks.
The “E” symbol on your smartphone means your phone is connected to your carrier’s 2G network. This usually indicates poor reception, as you would otherwise be connected to a 5G network, a 4G LTE network, or even a 3G network before falling back to 2G.
With 2G, your internet connection will practically crawl to a halt as you can get a maximum download speed of just 384Kbps. App experiences will suffer tremendously on any modern smartphone on 2G. So if you can connect to a Wi-Fi network, we recommend you do so.
EDGE vs 3G vs 4G LTE vs 5G: What’s the difference?
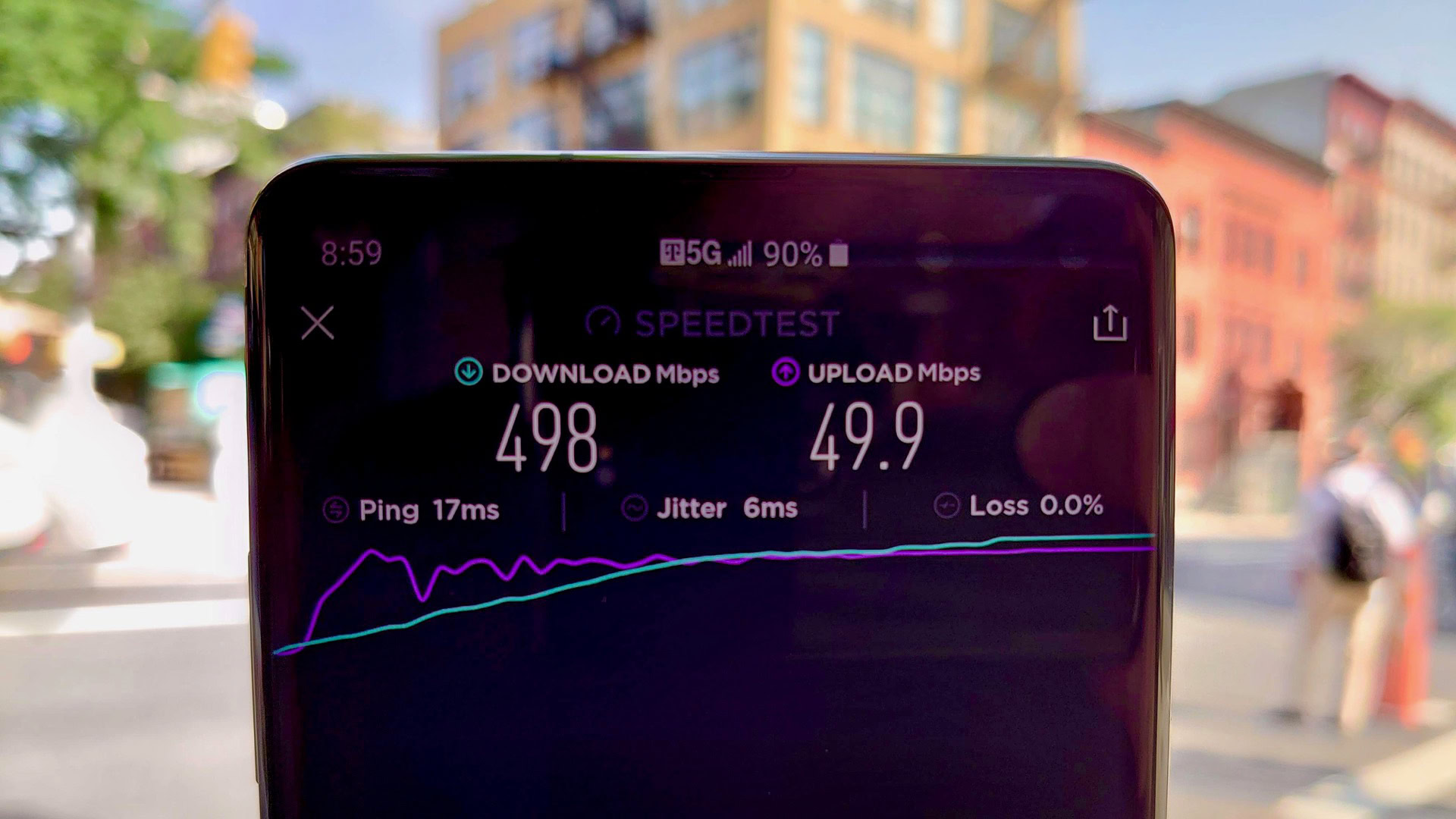
There’s a world of difference between these technologies, as each practically represents a different era of mobile network communication.
EDGE is a legacy 2G technology (often considered as pre-3G) and insufficient for the needs of today. In fact, it’s already been phased out in many parts of the world. 3G is the next step up in speed and bandwidth and what many regard as the bare minimum needed for a working smartphone experience.
As we go up the generations, the experience vastly improves. LTE and 4G are the most commonly found networks these days, providing a great smartphone experience. 4G is better than LTE, but both are often synonymously used and even referred to as “4G LTE” together. Then there’s 5G, the latest technology for cellular telephony, providing the best speed and bandwidth available right now, but at the cost of limited range.
Why is my phone not connecting to 4G LTE or 5G?
4G LTE is practically everywhere in urban cities worldwide, while 5G is also rolling out reasonably quickly to urban areas. Your phone will attempt to connect to 4G LTE or 5G networks (as per your device settings), and if those are not available, only then fall back onto 3G and 2G EDGE.
If your phone isn’t connecting to 4G LTE or 5G, it might be because you’re in an area with poor network connectivity (like a rural area). But if you are in a place where you usually get 4G LTE or 5G, it could mean that your carrier’s infrastructure has been overloaded. Simply put, the network capacity is full (as it usually happens in a crowded stadium during a major sporting event or concert).
Toggling airplane mode will force your phone to establish a new network connection.
Still, you can try forcing your phone to re-establish a network connection by toggling airplane mode. To do this, simply swipe down from the notification shade area on Android or expand the control center on iOS. Next, simply tap the Airplane Mode icon, wait for a few seconds, and tap it again. Under the right conditions, your phone should find a 4G or 5G link instead of falling back to 2G.
A 3G connection is what many consider the bare minimum, but that may not be sufficient for your needs if you are trying to access social media or upload photos or videos. If you are getting only a 2G signal, your experience will be even worse, and we would recommend that you stick to phone calls for communication.
How to change your preferred network type on Android
Here is how you can change your preferred network type on Android phones. Keep in mind that your phone will still fall back to 2G if it cannot find faster networks around you at any given point in time.
On Samsung Galaxy smartphones
- Go to Settings > Connections > Mobile networks > Network mode.
- Select 5G/LTE/WCDMA/GSM (auto connect). This option will connect to 5G, falling back to LTE when 5G is unavailable and going further down to 3G and 2G as needed. If you know you are not in the range of a 5G tower or have not subscribed to 5G data with your carrier, you should choose LTE/3G/2G, which will connect you to 4G networks as your primary choice.
On Google Pixel smartphones
- Go to Settings > Network & internet > SIMs > Preferred network type.
- Choose 5G here if you are subscribed to 5G and are in an area serviced by 5G. If not, LTE is a safe choice to get a good data connection.
If you want to turn off 5G, choose any of the other options. We also have a dedicated guide on how to turn off 5G on your Android phone in case you need further help.
How to change your preferred network type to 5G on iPhone
Here is how you can change your preferred network type to 5G on iPhones.
- Go to Settings > Cellular > Cellular Data Options > Voice & Data. Cellular may be labelled as Mobile in some regions, but the navigation path remains the same.
- You can choose 5G Auto, 5G On, or LTE.
- If you are subscribed to 5G, we recommend 5G Auto as it enables Smart Data mode. When 5G speeds aren’t needed, the iPhone will automatically switch to LTE to save battery life. 5G On always uses 5G, impacting battery life.
- If you are not subscribed to 5G services or spend most of your time in regions not serviced by 5G, then you should choose LTE.
- There is also a setting for 5G Standalone. When enabled, your iPhone will use 5G for all cellular activity, drawing more battery. Some carriers may need this setting enabled for 5G to work, so please get in touch with your carrier for the best setting.
FAQs
Yes, T-Mobile offered the last remaining 2G network in the US until September 2024. Verizon and AT&T shut down their 2G networks a few years ago.
You’re more likely to see the E or EDGE symbol at the edges of civilization where reception is hard to come by. Simply moving to an area with better 3G, 4G, or 5G reception will help get rid of the E symbol on the phone. For reference, EDGE indicates that you are connected to a legacy 2G network.
Your phone switches from 5G to E during periods of poor network reception or congestion in high traffic areas.