Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
Refresh rate explained: What does 60Hz, 90Hz, or 120Hz mean?
Published onOctober 15, 2024
High-end smartphones increasingly boast blazing-fast 90Hz, 120Hz, and even faster refresh rate displays. This sounds great on paper, and it’s yet another way that smartphones attempt to differentiate themselves from one another. Should you buy a phone because of this latest display tech trend? It honestly depends on where your priorities lie.
The benefits of high refresh rate phones and even how they work are not always well understood. While games and content can look much smoother, whether it’s worth the extra battery consumption depends greatly on the user and the handset. With that in mind, here’s everything you need to know about display refresh rates.
What is refresh rate?
Displays aren’t static. Content and motion appear smooth on your phone’s screen because every pixel constantly updates to display the latest content from your handset’s processor. But this doesn’t happen randomly. Panels update their content at regular intervals, which we refer to as the refresh rate.
The refresh rate measures the period of time between a phone’s display updates. In other words, how often and quickly the content on the screen refreshes. Measured in Hertz (Hz), the refresh rate counts the number of times the display fully refreshes every second. A 60Hz display refreshes 60 times per second, 90Hz is 90 times per second, 120Hz is 120 times per second, and so on. So, a 120Hz display refreshes twice as fast as a 60Hz panel and 4x faster than 30Hz.
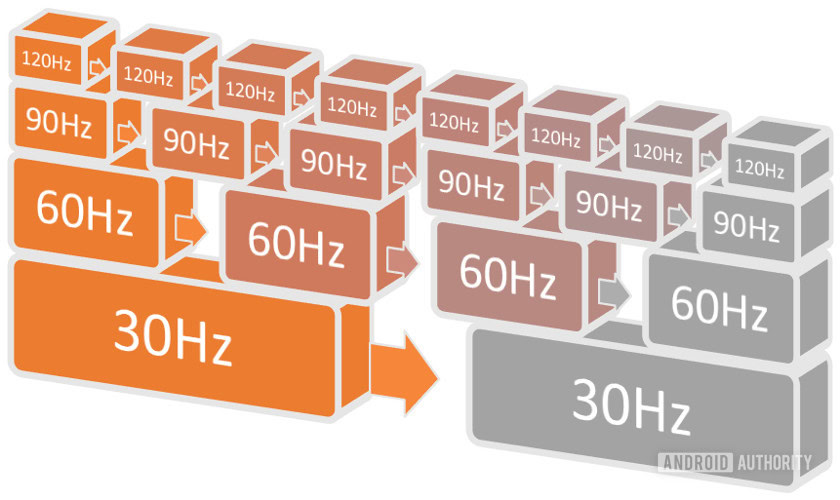
Faster update times also mean lower latency because the pixels refresh more often. For example, it takes 16.6 ms to entirely refresh a 60Hz display, 11.1ms for 90Hz, and just 8.3ms for a 120Hz rate panel. The refresh rate isn’t the only factor in round-trip display latency; it is the most significant contributor.
The refresh rate measures the period of time between a phone's display updates.
Your smartphone’s screen doesn’t refresh all at once each cycle, though. Instead, each horizontal row of pixels refreshes in turn until the whole display updates at the required rate. You can see this in action if you film a display in slow motion, and it’s the reason why displays flicker if you view them through your smartphone camera’s viewfinder. In other words, your display is constantly updating and refreshing, but it takes the cycle time to complete one full refresh. Check out this demo if you want to see how frame rates affect smoothness and motion blur.
A quick note on “touch sample rate” — a related but different metric. Also measured in Hz, the sample rate tells you how many times per second the touchscreen looks for input from the user’s finger. A higher touch sample rate means less lag between input (touch or swipe) and action, which is especially important for fast-paced games.
What does 60Hz, 90Hz, and 120Hz mean on my phone?
Higher refresh rate displays make moving content look and feel smoother and snappier. Even swiping through your emails and interacting with Facebook’s UI or your web browser can look smoother than the standard 60Hz rate. Although that’s not a game-changer for day-to-day smartphone use, it’s undoubtedly nicer to look at, and there are also more meaningful benefits to be found in fast motion content, such as video and gaming.
However, most films play at the industry standard of 24 frames per second or 24Hz (though this is changing now). As such, display processing needs to either adapt the frame rate to the content or upscale the content to the frame rate. 120Hz displays are great because they can playback content at 60Hz, 30Hz, and 24Hz with even frame divisions. Other refresh rates require processing when scaling 24Hz video. Poor quality processing can induce judder into your videos, which obviously isn’t good.
120Hz displays look silky smooth and feel more responsive at the cost of some battery life.
Faster displays make a big difference when it comes to gaming, too. Higher frame rates and quicker response times can have a noticeable impact because visual latency is lower, and gameplay appears smoother. PC gamers regularly swear by 120Hz and even 144Hz displays. Now, mobile gamers can benefit, too, albeit on a much smaller screen. However, high frame-rate gaming requires a beefy, energy-hungry processor, too. This ensures that the graphics frame rate keeps up with the high display refresh rate. The game you’re playing also needs to support high refresh rates. A 120Hz display won’t benefit from a game capped at 30 frames per second.
Unfortunately, high refresh rates reduce battery life. We once looked into this with the OnePlus 7 Pro, and we noted 200 fewer minutes of browsing time when using the 90Hz mode versus the more standard 60Hz. We also recorded a 9% drop in battery life when switching the Galaxy S20 Ultra between 60Hz and 120Hz modes. However, newer handsets with more efficient displays provide decent battery life, thanks to adaptive 90Hz and 120Hz refresh rates. This is helping to lessen the trade-offs associated with early high refresh rate panels.
Smartphone variable refresh rates: What is LTPO?
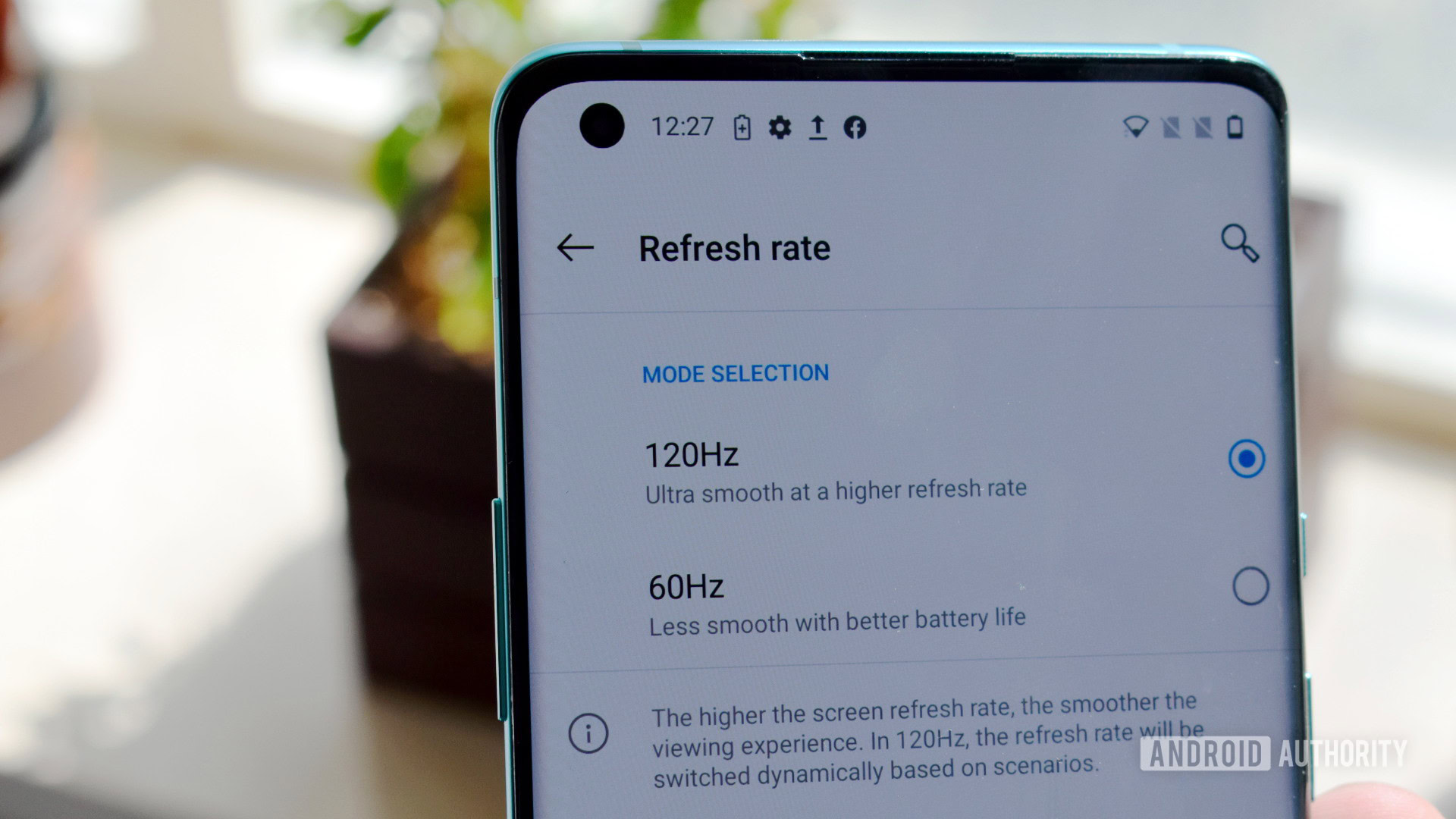
Higher refresh rates negatively impact screen-on time, but manufacturers have come up with some clever technologies to limit their impact on battery life. Variable refresh rate AMOLED panels powered by low-temperature polycrystalline oxide (LTPO) backplane technology are leading this revolution.
Flagship phones pack LTPO displays to save battery while still offering high refresh rates.
Implementations vary, but a combination of LTPO and software changes allows for dynamic refresh rates actively ranging from 120Hz down to 1Hz, although in reality, lowering refresh rates to 60, 24, and 10Hz is more common. The idea is simple in principle: reducing the number of display updates when viewing static content, such as images and web pages, improves battery life while still benefiting from the smoothness of very high refresh rates when scrolling through content.
Examples of LTPO variable refresh rate phones that can hit 10Hz and lower include the Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra, Pixel 9 Pro, and the OnePlus 12. Samsung also employs a novel technology in its Galaxy S23 and S24 series phones. The display refresh rate drops as low as 48Hz, but communication between the processor and display falls as low as 10Hz to save on some more power.
Should I buy a high refresh rate phone?

120Hz displays are now a mainstay in modern smartphones, not just in the ultra-premium market. These panels are increasingly available in affordable mid-tier handsets, as well as some budget options.
That said, refresh rate is a small part of a smartphone’s display specifications. You shouldn’t buy a fast display if the color is awful. Ultimately, aspects like color gamut, contrast, white point and color temperature, HDR capabilities, and resolution significantly impact your phone’s screen quality. That said, high refresh rates are now a big selling point in modern mobile displays and are increasingly hard to ignore when picking up a new phone.
If you have your heart set on a lightning-fast display, here are just a few of the latest and greatest phones rocking a quick panel that we recommend.
Great phones with high refresh rates:
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra ($1419.99 at Amazon): Samsung’s new flagships continue to run 120Hz displays, but we also love the brightness of the company’s displays.
- Google Pixel 9 series ($1099 at Amazon): Google offers 120Hz refresh rate screens across its Pixel 9 devices.
- Google Pixel 8a ($499 at Amazon): The Pixel 8a is the first Pixel A-series phone to pack a 120Hz display.
- ASUS ROG Phone 8 ($1099 at Amazon): A 165Hz panel is the star of the ROG Phone 8, but you may not find too many games able to take advantage of that refresh rate.
- Samsung Galaxy A55 5G ($387 at Amazon): Samsung’s mid-range phones now regularly feature high refresh rate 120Hz AMOLED panels.
Nearly all smartphones on the market support higher than 60Hz refresh rates these days, so you won’t have to look very far. Exceptions are very rare now.