Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
Back To Basics: Screen technology explained
June 26, 2013

This week’s edition of Back To Basics is going to focus on the part of your device that you’re spending almost all your time looking at. It’s time to talk screen technology.
No two displays are the same, but there are a few guidelines that can help you choose the right screen for you. From the screen resolution, pixel density, type of display, to even the size, there are a lot of factors that determine whether a display is good or not, but fear not, read on as we explain what to look for in a smartphone or tablet display.
Screen resolution and pixel density
The first thing you might hear about your display is the screen resolution and pixel density or PPI (pixels per inch). Due to the vast size and price range of Android devices, there are a wide variety of screen resolutions, so we’ll cover the most popular ones.
Screen resolutions are commonly written as width x height (e.g: 800 x 480 means that the display is 800 pixels wide, and 480 pixels tall). Here are some of the most popular screen resolutions:
- 240×320: This screen resolution is most commonly used on really small screens, and/or on budget phones.
- 320×480: This screen resolution is also used on really small screens (sub 4-inch), and/or on budget phones.
- 480×800 (WVGA) : A few years ago this was the premier screen resolution and as such was found on many high-end phones like the Samsung Galaxy S2, but now it’s usually reserved for mid-range smartphones with displays that are smaller than 5-inches.
- 960×540 (qHD): This was also a high-end screen resolution a few years ago, but is now reserved for mid-range smartphones.
- 1280×720 (HD/720P): To be classified as a high-end smartphone last year you would need a HD display. Some mid-range and high-end smartphones and tablets will be found with this screen resolution.
- 1920×1080 (Full HD/1080P): Usually reserved for TV’s, Full HD smartphones have come up in a big way this year. A Full HD display is currently exclusively available on high-end smartphones and tablets.
- 2560×1600 (WQXGA): This is an insanely high resolution which is currently found on the Nexus 10, and is exclusively available on high-end tablets.

When it comes to screen resolution there are a lot of factors. On smaller displays and cheaper smartphones you’ll see lower screen resolutions, and on larger displays or high-end devices you’ll see higher screen resolutions.
Pixel densities are important when it comes to the overall sharpness or the display, which is important for reading web pages or e-books. Pixel densities vary due to the screen resolution and size. If the display is large, but the resolution is low, the PPI (pixel per inch) count will be lower.
A pixel density higher than 300 PPI is great, a pixel density lower than 100 PPI is considered poor, and a pixel density between 200 and 300 PPI is considered reasonable.
It’s a widely held belief that a pixel density above 300 PPI is considered great, and most won’t be able to see any jagged lines, or pixels. A pixel density lower than 200 is considered poor and is usually found on low-end devices, and a pixel density between 300 and 200 is considered reasonable and is usually found on mid-range devices
What is an LCD display?
LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display, and is the most popular display type for mobile devices. This is due to its relatively low power consumption and good image quality.
TFT Display
The most popular type of LCD display is the TFT display, which stands for Thin Film Transistor display. This display tends to be the best type of mobile LCD displays.
TFT displays provide greater contrast and improve response time, however are more expensive, and less power efficient.
It has a transistor next to every pixel, and therefore allows each individual pixel to be turned on and off. This improves response time and provides greater contrast than other types of LCD displays. However, they also tend to be the most expensive, and less power efficient.
IPS panels
Some high-end smartphones and tablets use an IPS (In-plane switching) panel which is a type of TFT panel, but improves upon some of the drawbacks of a regular TFT LCD panel. IPS panels produce consistent and accurate color from all angles. Therefore, they have wider viewing angles than regular TFT displays, which is great for people who watch videos with a group of friends.
Super LCD
Manufactured by Samsung, but used mostly by HTC, Super LCD is a display technology which removes the air gap between the outer glass and the display elements. This reduces the glare, and also consumes less power and has better outdoor visibility than regular LCD screens.

The latest version of Super LCD is Super LCD3 and is said to consume less power than previous versions. It is found on the HTCButterfly, HTCDroid DNA and HTC One.
What is an OLED display?
OLED stands for Organic Light-Emitting Diode, and an OLED display consists of organic polymer which lights up when charged with electricity. It offers many advantages over LCD displays as it is thinner, brighter, more power efficient and provides wider viewing angles. They also provide much better contrast and response times.
The most popular type of OLED panels on mobile devices is AMOLED technology. AMOLED stands for Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode and is even more power efficient than standard OLED displays.
The largest manufacturer of AMOLED displays is Samsung, which markets its displays under the Super AMOLED moniker. Most of Samsung’s high-end and flagship smartphones use Super AMOLED panels, however some use LCD panels.
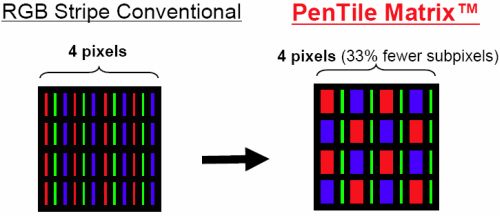
Samsung has sometimes used a PenTile matrix on its displays. This uses two subpixels inside every pixel in a RGBG (Red-Green-Blue-Green) structure, instead of the standard RGB (Red-Green-Blue) structure. Some have criticized PenTile displays for overall fuzziness, but most agree that at higher pixel densities the fuzziness is not apparent. The PenTile matrix is used by Samsung for longer life of display, as the blue subpixel degrades faster than the other subpixels in OLED panels.
AMOLED VS LCD: Which is for you?
Both display technologies offer advantages and disadvantages. AMOLED screens have higher contrasts and deeper, true blacks, but LCD’s tend to offer more accurate colors. While AMOLED displays are brighter when viewed off-center, LCD panels can be viewed more easily under direct sunlight.
AMOLED displays tend to be more power efficient overall, however, LCD panels are more power efficient when it comes to displaying web pages. AMOLED screens have better viewing angles, but LCD panels tend to be sharper on lower resolution panels thanks to the use of the RGB structure instead of PenTile RGBG.

Of course, people looking for a budget smartphone won’t find many devices utilising AMOLED displays (unless they are older Samsung Galaxy S smartphones), so they would be looking at LCD panels. People looking for mid-range devices will face the same situation, however, there are a few devices available using AMOLED displays. In the high-end market for smartphones there is a bigger question on which display technology is best.
Wrap up
Overall, it depends on whether you prefer the true blacks and high contrast of AMOLED displays or the accurate colors and direct sunlight performance of an LCD panel. In the tablet market there is no doubt as to which display you should use, since the tablet market almost exclusively uses LCD panels.
Thank you for being part of our community. Read our Comment Policy before posting.