Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
What is USB Type-C? Or is it USB C?
Published on7 hours ago

If you’ve bought a new smartphone, tablet, or even laptop in the past few years, chances are it has a new port used for fast charging, data transfer, and even audio-out. The new port is officially called USB Type-C and as you’ve probably noticed, it’s completely reversible and present on a wide range of devices!
Of course, there’s much more to this new connector than just a reversible version of the old micro-USB design. So in this article, let’s take a look at exactly what USB Type-C is, what it can do, and why it matters.
What is Type-C: The first reversible USB connector
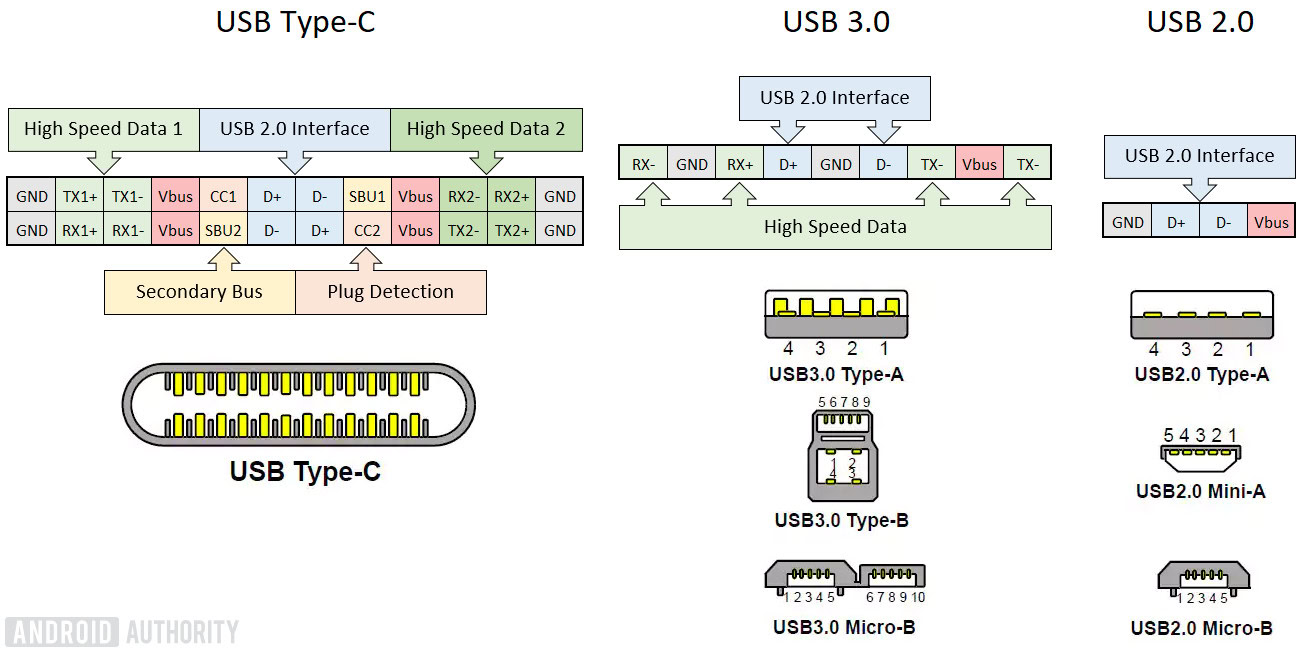
First, a quick history lesson. The USB connector goes all the way back to 1996 with the larger USB Type-A connector that you will probably still find on your PC and laptop. But while the shape hasn’t changed in 30 years, it has seen numerous revisions to improve its speeds and capabilities. The micro-USB port came along with USB 2.0 in 2000 and was the connector port of choice for the vast majority of portable gadgets until USB Type-C came along in 2014.
USB Type-A, B, micro, and mini all share the same basic internal electric connections (it’s just the port shape that varies). Faster 3.0 cables and ports boast an extra high-speed data lane, though. USB Type-C triples the pin count from USB 3.0’s eight up to 24. So as well as being the first reversible design, USB Type-C also greatly expands the number of pins and thus its capabilities too.
USB is almost 30 years old, but Type-C is the first reversible cable and major revamp of the standard.
Despite the huge increase in the pin count, USB Type-C is a very small connector that takes up no more room than an old USB micro-B port. This is partly why it’s been adopted so quickly in smartphones, albeit to different specs and standards. It’s also present in a wide variety of other portable gadgets, ranging from desk lamps to electric trimmers.
As you probably spotted on the diagram above, USB Type-C is backward compatible with USB 3.0 and even older 2.0 cables, as it still features the pins used for these traditional data protocols. You’ll find plenty of Type-C to Type-A and micro-B cables for sale online. However, you won’t be able to use some of the advanced features of USB Type-C when using these cables, and that situation has led to some problems when it comes to obtaining quick charge speeds from smartphone chargers.
USB-C is short for USB Type-C, which is the latest standard used for charging and data transfer in gadgets like smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
How fast is USB Type-C? Power and data speeds explained

It’s easy to equate Type-C with fast data transfer, but there are notable differences between USB-C and USB 3.2. Initially, USB Type-C was designed to offer the same speeds as USB 3.2 Gen 2, hitting up to 10 Gbit/s data transfers. That’s twice as fast as a standard USB 3.1 Gen 1 port (or USB 3.0) that offers 5 Gbit/s. It’s also more than 20x faster than USB 2.0’s 480 Mbit/s data speeds.
The switch to USB Type-C should have simplified this complicated situation, ensuring that newer devices all operate with the fastest possible speeds. However, due to demands for backward compatibility, only some fully-featured USB Type-C ports and cables guarantee USB 3 data speeds, and there are a number of devices out there that still only offer USB 2.0 data speeds over this new connector. For example, the base iPhone 16 has a USB-C port but can only transfer files at USB 2 speeds. You can reference the chart below to see just how slow USB 2.0 is relative to newer standards.
USB Type-C is no guarantee that you'll see the fastest available data speeds.
In addition, the Type-C connector is also used by the Thunderbolt 5 and USB 4 standards. These offer even higher peak data transfers at up to 40 Gbit/s and support multi-monitor connections over the same Type-C connector. However, it’s worth remembering that if you’re connecting to backward-compatible ports via a converter cable (such as Type-C to Type-A), you will be limited to the slower speed of the older port.
Besides delivering data, USB Type-C is designed to power all of our gadgets. The connector is rated to deliver and receive up to 240W of power, making it suitable for charging laptops and more. Things do get a little complicated here though, as there are multiple different standards and protocols that can be used to power USB devices. Devices have to negotiate or ask to receive higehr power levels, so simply owning a charger capable of delivering 240W isn’t enough. Both sides have to support the required charging level.
By default, USB 2.0 ports offer up to 5V, 0.5A of power and 3.0 ports extend this to 5V, 0.9A. USB Type-C pushes even further when connecting two of the ports together, with options for 1.5A and 3.0A worth of current. Again, there are no guarantees about the exact level of power you’ll receive from any particular port just by looking at the connector, but Type-C theoretically offers higher speed charging out-of-the-box than other options.
In addition to the default power options, Type-C devices can be fully compatible with the USB Power Delivery specification. This can be used to augment the basic charging options with even higher power delivery all the way up to 240W. However, Power Delivery isn’t limited to Type-C devices and could still work when connecting up to Type-A or other connectors that also support the optional specification.
The bottom line is that USB Type-C devices should enable faster data transfers and charge times than previous models. However, the exact specifications depend on what the manufacturers decide to implement and aren’t intrinsically linked to the port type.
The biggest USB Type-C advantage: One port for everything

In addition to power and data, USB Type-C is designed to support a wide variety of different modes and standards too, positioning it as a one-size-fits-all solution for a selection of technologies. A number of audio and video modes are supported, setting up the connector to become a replacement for the 3.5mm headphone jack and the HDMI cable.
For audio, the connector supports digital audio via the USB Audio Class specification, of which version 3.0 is the latest. Analog headsets are also supported over the connector through the Audio Adapter Accessory Mode, which repurposes the port’s SBU and CC pins for left, right, and microphone connections. With a pass-through connector, devices can also be charged up with 5V/500mA worth of power.
USB-C supports both audio and video standards over the connector too.
Video over the connector can come in a number of different forms, including the HDMI, superMHL, and DisplayPort standards. These are enabled via Alternate Mode which frees up the SBU and high-speed data pins for use with other standards. HDMI Alt-mode is available via a converter cable, enabling up to a 4K resolution, surround sound, and even 3D content playback.
Display Port over USB-C is supported with both USB 2.0, 3.1, and Thunderbolt specced connectors, offering up to 4K 60Hz 24-bit HDR playback, a maximum 8K resolution, and multi-channel audio. Finally, superMHL again works with USB 2.0 and 3.1 speeds over the Type-C connector, with 4K and 8K resolutions at up to 60fps supported on fast enough setups. Dolby Atmos surround sound is incorporated, as is backward compatibility with existing MHL specifications.
However, all of these modes also require additional hardware and software support behind the port, so checking the compatibility of your device is a must.
Is it USB-C or USB Type-C? A wrap-up
While USB Type-C is the official name for the standard, mainstream usage often drops down to just USB C. In many articles on Android Authority and throughout the web you’ll probably hear a bit of both. No one way is wrong, although USB Type-C is technically more accurate.
As you can see from all of the above, USB Type-C is a complicated connector and not just in its physical design. The standard provides a wider range of possible implementations than ever before, ranging from faster data and power speeds to extra optional multimedia features. We’re also starting to see the port appear on all kinds of electronics, from Bluetooth speakers to even toothbrushes!
USB Type-C is often shortened to USB-C and both mean the same thing.
While this wide range of options is part of the standard’s appeal, it’s also one of the more complicated connectors for consumers to understand. A single connector with many features sounds great, but the optional nature of support makes it impossible to tell what a port or cable is capable of just by looking at it. The level of research required by consumers to make sure they buy the right USB Type-C products and cables is higher than for its predecessors, and that’s not a good thing.
There’s much more to USB Type-C than just a reversible connector. Funnily enough, though, it’s probably that feature alone that makes the port so appealing for portable consumer electronics. If there’s anything you should take away from all of this, it’s that you’ll probably only need one cable to charge every device you carry around.
FAQs
The easiest way to check if your USB is Type-C is to inspect it for symmetry. If it’s oval shaped with pins in the middle, you’re mostly looking at USB Type-C. On the other hand, if the port has sharp corners, you’re dealing with a different USB port.
The iPhone does not use USB-C yet, even though virtually all Android phones and even iPad models use it. That said, we expect Apple to switch over soon.
Lightning and USB-C are not the same. Apple developed Lightning for its own products and eventually moved to USB Type-C starting with the iPhone 15 series. Meanwhile, USB-C has no brand restriction or control as it is a universal standard.