Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
What does 5G UC mean? Is it better than regular 5G?
Published onNovember 4, 2024

If you’re a T-Mobile customer in the US, chances are that your smartphone has displayed a 5G UC badge at some point. While most of us already know that 5G is the successor to 4G LTE, the exact differences between various types of 5G aren’t often talked about. Here’s everything you need to know about the 5G UC logo on your smartphone and how it differs from other network variants like 5G UW.
T-Mobile uses the 5G UC branding, short for Ultra Capacity, to refer to its fastest networks on Android and the iPhone. Unlike regular 5G networks, you can expect faster speeds than 4G LTE as well as better reliability in crowded areas.
What is 5G UC?
Not all 5G networks are equal — you can get a vastly different experience from one area to the next, both in terms of speed as well as range. This is because the network spectrum is utilized differently in each area.
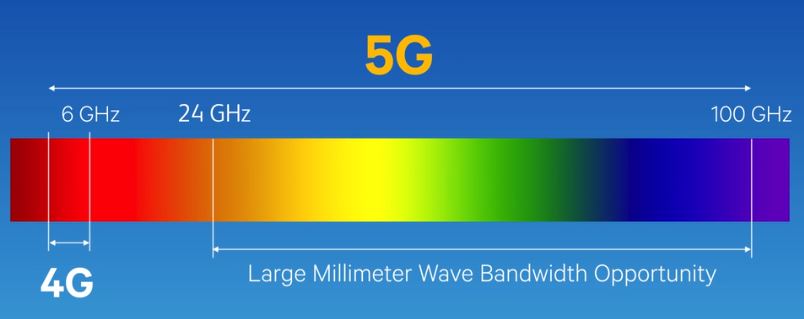
In simpler terms, a 5G network can be either low-band, mid-band, or mmWave. T-Mobile has two different types of branding to distinguish between these flavors, namely XR and UC.
5G XR and UC indicate two different types of 5G.
T-Mobile refers to low-band 5G deployments as Extended Range 5G, or 5G XR. Much of the company’s “nationwide 5G coverage” claim is built on top of the low-band part of the 5G spectrum.
Low-band 5G is the least exciting 5G band as it operates on many of the same frequencies as 4G LTE. This means that you cannot expect blazing fast speeds, but it does offer latency improvements. It also offers far better coverage than the other two bands. You’re most likely to find low-band 5G in less developed areas as it requires less expensive infrastructure.
If you live in a big city, however, you may find your smartphone picking up a 5G UC signal. This label indicates T-Mobile’s mmWave and mid-band 5G deployments.
mmWave and mid-band are at the other end of the spectrum as low-band, quite literally, and are sometimes referred to as C-band 5G. These operate at much higher frequencies than prior cellular generations. They not only enable real-world 5G speeds of nearly 1 Gbps but also reduce the chances of congestion in crowded areas.
5G UC indicates your phone is communicating over the fastest mmWave or mid-band frequencies.
Indeed, mmWave is what you might think of when visualizing the jump from 4G to 5G. However, it’s not omnipresent. High frequencies suffer from limited range, so they’re best deployed in dense urban environments. Even then, obstacles like walls can have a large impact on signal strength. And if your phone has poor signal strength, even just leaving 5G enabled can impact battery life.
Finally, we have mid-band 5G. Simply put, it’s the middle ground between mmWave and low-band 5G. It offers small improvements over 4G while still maintaining coverage over large areas.
Is 5G UC faster than regular 5G?
Yes, T-Mobile’s 5G UC networks are indeed faster than regular 5G in the sense that it uses higher frequencies, including mmWave (pictured above). It will also always offer better-than-4G speeds. On the other hand, the company’s Extended Range 5G (5G XR) relies on lower frequencies. This means it is designed to cover large areas like 4G did. It does not prioritize speed to the same degree as UC.
The trade-off with 5G UC is that you will only find it in major cities because of the high infrastructure costs and limited range. You can check if your neighborhood has 5G UC coverage by checking T-Mobile’s coverage map.
5G UC offers faster speeds, but it doesn't tell you if you're on the fastest possible network band.
However, the UC logo on your smartphone doesn’t tell you whether you’re connected to the fastest possible band. This is because only a handful of smartphones have the required hardware for mmWave 5G. If your smartphone only supports sub-6GHz 5G, you’ll still get 5G UC but only up to mid-band networks and not beyond.
As a rule of thumb, most flagship Android phones as well as recent iPhone models sold in the US have full support for 5G UC, including the highest-end mmWave bands. Moving down the stack, you’ll still see the 5G UC on smartphones around the $500 price point, but these devices will likely rely on mid-band frequencies. You can still expect real-world 5G speeds in the hundreds of megabytes per second, a decent improvement over 4G LTE.
5G UC Vs. 5G UW Vs. 5G+: How do they compare?

In the US, every carrier has its own label for mid-band and mmWave 5G deployments.
- T-Mobile: The 5G UC branding indicates high-speed 5G. 5G XR points to longer range networks that prioritize signal strength over top speed.
- AT&T: Look for the 5G+ or 5G Plus badge in your phone’s status bar to know if you’ve connected to a mid-band or mmWave frequency band.
- Verizon: Verizon chose to create its own UW branding, short for Ultra Wideband, to denote high-speed 5G connectivity. Be careful to not confuse it with the UWB tech that’s present in many high-end smartphones today.
To summarize: 5G UC, 5G+, and 5G UW all mean the same thing and will get you the fastest transfer speeds for that carrier. That said, regular 5G will still do the job outside of crowded arenas and sporting events, so you don’t have to worry about which logo your smartphone shows at any given time.
Want to experience T-Mobile’s 5G UC network when its available? Sign up for a plan below! Want more information on what plans T-mobile offers? Be sure to check out our guide to the best T-mobile plans.
FAQs
5G UC stands for Ultra Capacity 5G. It is T-Mobile’s branding for mid-band and mmWave 5G networks.
On T-Mobile, 5G UC is faster than regular 5G since it uses higher frequencies than regular 5G (also known as 5G XR). The same is true for Verizon’s 5G UW and AT&T’s 5G+ networks.
5G Ultra Capacity (5G UC) relies on mid-band and high-band frequencies that aren’t very commonplace outside big cities. If your smartphone has to constantly hunt for a signal, you may see inferior battery life compared to standard 5G or 4G LTE.
UC stands for Ultra Capacity, or T-Mobile’s higher frequency 5G signal for faster speeds and lower congestion.
Not all smartphones support 5G UC, so you may need a newer model. Likewise, you may only see 5G UC in urban areas with regular 5G deployed in less populated regions.
If you find 5G UC too slow, try forcing your phone to use 4G. A strong LTE signal can sometimes outperform a weak 5G UC signal.
To turn off 5G UC, head into your phone’s Settings app, then navigate to Connections > Mobile Networks > Network Mode. Here, you can select between 4G and 5G networks.