Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
What is blockchain technology and how does it work?
Published onAugust 5, 2022
If you’ve ever read about cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, you may have come across the terms blockchain or distributed ledger. You’ve probably also heard about how corporate giants like Walmart and Visa are testing the technology, either to improve traceability or accountability.
Given the amount of hype surrounding it, you’d think that blockchain technology is rapidly shaping up to become one of the most influential technologies of this decade. Despite how disruptive it seems on the surface, however, there is still some confusion over what exactly it accomplishes. Moreover, some argue that the technology’s recent applications in the private sector are forced, or mere gimmicks.
In this article, we take a closer look at the technology’s underpinnings and its close relationship with the cryptocurrency ecosystem. Later, we’ll also discuss if blockchains have any merit in the context of private companies and government organizations.
What is blockchain technology?

The core functionality of blockchain technology was first conceptualized decades ago. Between 1982 and 1992, various researchers theorized that a “chain of blocks” could be used to store and share document timestamps in a tamper-proof manner.
It took nearly 20 more years for the technology to find a practical use case in the form of Bitcoin. Its creator, Satoshi Nakamoto, borrowed the researchers’ original idea of creating a tamper-proof chain of data — the primary difference being that the chain would record monetary transactions instead of timestamps.
The origin of modern blockchain technology can be traced back to Bitcoin.
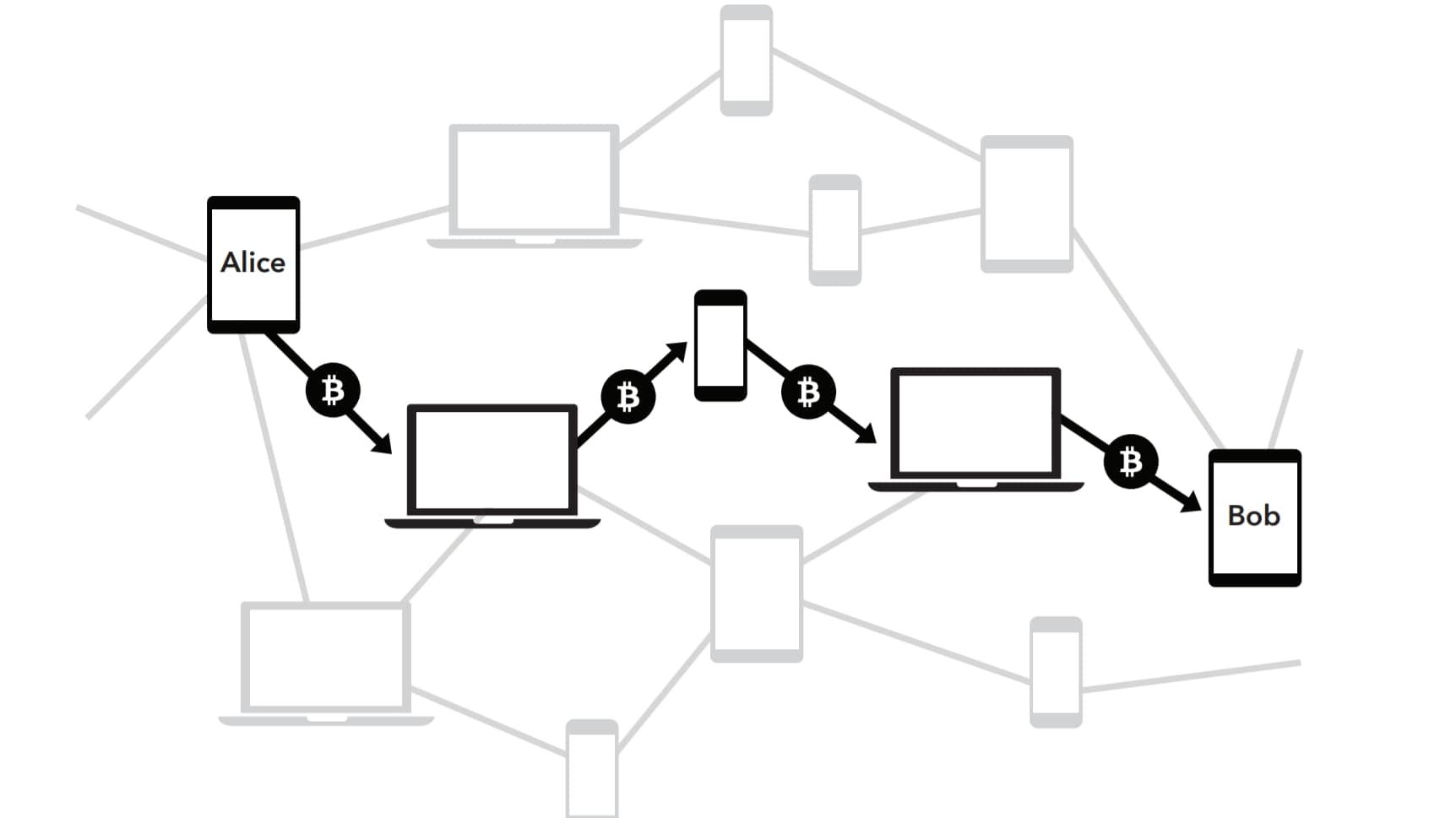
Nakamoto figured out a way to share Bitcoin’s transaction records between strangers in a completely trustless manner. An individual could tell with absolute certainty whether a particular copy of the blockchain was legitimate or not. Perhaps more importantly, this could be done without any involvement or guidance from a trusted authority, third party, or intermediary. This breakthrough was named proof of work and forms the bedrock of today’s decentralized cryptocurrencies.
In a nutshell, proof of work imposes specific rules and restrictions on how new transactions are recorded to the blockchain. Why is this necessary, you ask? Simply put, it prevents malicious actors from adding illegitimate transactions to the ledger. An example would be spending more bitcoin than you own or repeating previous transactions. There’s even a name for this — double-spending.
Read more: What is Bitcoin and how does it work?
The definition of a blockchain is pretty simple. It’s essentially a ledger of transactions, shared and replicated across a network of computers. It can also be updated in a trustless manner, which means you don’t need a central authority or trusted verifier.
What are the advantages of blockchain?
Blockchain’s legacy aside, why is it so important if it just boils down to a growing list of transactions for digital currencies? Here are a few key advantages the technology offers over traditional methods of data storage, like databases:
- Tamper-resistance and immutability: Decentralization is the primary goal of blockchain technology. In a nutshell, this property means that new data can only be added or modified if a majority of the network agrees to the change. No individual or entity can feasibly corrupt or reverse this process for self-gain. That said, not all blockchains are equally tamper-resistant — private ones can suffer from centralization and, therefore, lack this property.
- Transparency: Every single update and addition to a blockchain is publicly viewable. This improves the record’s credibility over traditional alternatives that don’t have any mechanism to audit or verify past changes.
- Permissionless: Public blockchains allow anyone to participate, and everyone has equal access and rights. Because of their distributed and decentralized structure, they cannot be shut down or censored.
- No single point of failure: Replicating and sharing data between strangers enables redundancy. For example, in the case of popular blockchains such Bitcoin, the record can survive even if entire continents go offline.
How do blockchains actually work?
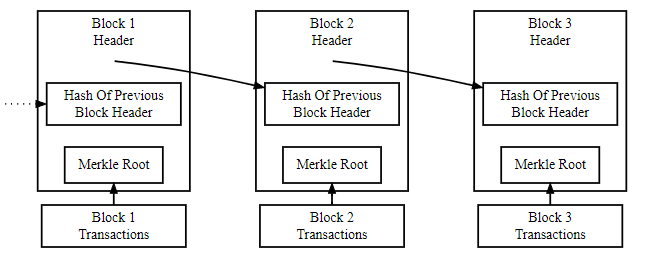
With the general definition out of the way, let’s delve into a technical overview of blockchain technology. Let’s start with the basics. Remember how we described blockchain as a digital record of transactions? Consider that a bit of a simplification. Rather than thinking of blockchains as a list of separate or discrete entries, imagine them as bundles of transactions instead. One such bundle is called a block and usually includes other relevant data such as the timestamp.
A blockchain is made up of blocks, which are just bundles of data or transactions.
With these guidelines alone, it’s easy to see how a blockchain is formed.
If you line up these transaction bundles one by one, using the included timestamps, you can establish a chronological order of blocks. The result is a really long list of blocks, dating back to the original block. In the cryptocurrency community, this first block is commonly referred to as the genesis block.
So a blockchain is a list of transaction blocks, ordered by date and time. But that’s only half the story. What if a dishonest individual came along and offered a different record of transactions that are fake but have valid timestamps?
This is where cryptographic hashes come into play and where cryptocurrency got its name from.
Cryptographic hash functions: Keeping blockchains honest

Within every block on a blockchain, you’ll find a unique identifying hash. A hash is simply the result of a mathematical function or algorithm. More specifically, it’s a result of the SHA256 hash function.
While this may sound complicated, it’s really simple in practice. All the hash function does is take some data as input and generate a unique output. Take the text Hello world! for example. This is the hash you get for it:
c0535e4be2b79ffd93291305436bf889314e4a3faec05ecffcbb7df31ad9e51a
Even a minor change in the input — like swapping an uppercase letter for lowercase — would completely change the hash.
In the context of blockchains, anyone can easily detect if the contents of a block have been tampered with. Each new block added to a blockchain includes a reference to the previous block’s hash. That block, in turn, contains the hash for the preceding block, and so on.
If you’re wondering how including the previous hash deters attackers, it’s because computing the solution to a hash function is not easy with large cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Furthermore, since each block’s hash depends on the previous block’s hash, changing a past transaction requires redoing the computation for all of the blocks between then and now.
Without getting into the specifics of how cryptocurrencies work, generating a hash for a single Bitcoin block takes ten minutes on average. And that’s with thousands of highly specialized computers performing hash calculations.
Satoshi Nakamoto explained this hypothetical situation in the Bitcoin white paper as well:
If a majority of CPU power is controlled by honest nodes, the honest chain will grow the fastest and outpace any competing chains. To modify a past block, an attacker would have to redo the proof-of-work of the block and all blocks after it and then catch up with and surpass the work of the honest nodes.
Continue reading: What is Bitcoin mining and why is it so important?
Incentivizing honesty
Volunteers are typically incentivized to participate in a blockchain’s hash calculation process in exchange for a reward. In the case of Bitcoin, the reward is a minimum of 6.25 BTC — worth hundreds of thousands of dollars today. However, only one validator among hundreds or thousands wins the reward from each block. Everyone else has to start over and try again.
See also: How to mine Ethereum on a gaming PC
Through this competitive process, blockchain networks gain diverse participation, further strengthening them. If a hacker were to try and outperform other honest participants, they would need over 51% of the entire network’s hashing power or hash rate.
If someone shows up with an incorrect record — or even just a single block with incorrect transactions — every other participant can easily spot the hash discrepancy and reject their copy of the blockchain. There is simply no incentive for them to side with the attacker.
Blockchain consensus mechanisms: What’s next?

While the aforementioned proof of work system works exceptionally well, it suffers from one major problem: scalability. The proof of work algorithm that we’ve discussed so far is designed to generate a block every fixed amount of time — 10 minutes in the case of Bitcoin, 12—15 seconds in Ethereum, and 2.5 minutes in Litecoin.
However, the system is so astoundingly competitive that we now have entire farms of computers dedicated to earning the block reward. Transaction validators are almost always incentivized to keep increasing their computational power to improve their chances of winning a reward.
Despite these increased computational contributions over the years, blockchain networks can’t actually process any more transactions. Validators are in the business of computing hashes for the reward, not verifying individual transactions.
This is a major problem for many of the aforementioned cryptocurrencies. A global payment system needs to support thousands of transactions per second, with the ability to scale even beyond.
However, proof of work’s scalability limitation is a staunch design choice, with the goal of promoting decentralization. Still, this stalemate has motivated many critics to find alternative approaches that do not involve competitive hash calculations.
So far, no all-encompassing alternative has presented itself. As a stepping stone to scalability, though, we have some cryptocurrencies like Cardano using alternative mechanisms. Proof of stake is currently regarded as one of the best alternatives.
What about private or permissioned ledgers?
So far, we’ve only discussed blockchains from the perspective of the cryptocurrency ecosystem. As we alluded to earlier, though, the technology has found appeal in the most unlikely of places — private companies and governments. Blockchains don’t have to record financial data; they can just as easily hold any other kind of data.
Even though Bitcoin was created to directly compete with financial institutions, banks themselves are now looking to use the underlying technology for faster international transactions and potentially reduce human oversight.
Unlike cryptocurrency blockchains, private implementations are permissioned. This means that they are usually only accessible by a select few, and transaction records are not publicly available or auditable. Some examples include the Hyperledger Fabric and Corda platforms.
So far, several high-profile companies have jumped on the blockchain bandwagon. Walmart, for instance, tested the technology in a bid to improve the traceability of food products. On the other hand, DHL worked with Accenture to develop a blockchain for pharmaceutical supply chains. In its press release, the German logistics firm said,
Using a common, indelible and secure ledger, the industry can achieve much higher safety standards – from the factory to the patient – at much lower cost. This is one of several opportunities blockchain affords to restructure business processes while reducing cost and complexity.
Do private blockchains make sense?
Even after several years of public discourse and debate, there is no clear consensus on the usefulness of private blockchains. This is because implementations can vary significantly between companies. Furthermore, the mere existence of a blockchain does not address prevalent issues such as tampering and lack of traceability.
Indeed, the technology can help reduce overhead costs, but without public transparency, there’s no way to know if a particular blockchain record is trustworthy or not. Remember that blockchains rely on a diverse set of stakeholders to achieve consensus. In the case of private and permissioned blockchains, this is conspicuously absent.
Private blockchains often fail to deliver decentralization and transparency.
In other words, permissioned blockchains require you to trust the security practices of a third party or authority — the exact antithesis of most public blockchains like that of cryptocurrencies.
Does this mean that private blockchains are a fruitless endeavor? Not quite — you still get a few advantages, namely high availability and the ability to maintain a permanent, time-stamped record of data.
Furthermore, even if consensus is locked to the company that owns the blockchain, the risk of data loss or tampering is distributed across more than one computer. Hackers cannot infiltrate the system through just one central server — they need to pull off a simultaneous attack instead. This is why the technology is often referred to as distributed ledger technology in the context of private applications.
In other words, the merits of such private applications are realized simply by storing copies on multiple computers around the world instead of reaching an agreement between a diverse set of stakeholders.
Blockchain applications beyond cryptocurrency

In recent years, blockchain platforms like Ethereum have enabled alternative use-cases of the technology — including decentralized finance (DeFi), property rights management, digital identity, and supply chain management.
On the decentralized finance front, blockchain-based finance platforms shine in areas with fragmented or underdeveloped infrastructure. Services like lending, insurance, and savings can now exist among demographics and geographies that would otherwise be unserviceable by banks. Besides lowering the barrier to entry, DeFi services require no middlemen, resulting in pretty big reductions in processing fees and timelines.
Read more: What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
The world also recently got a glimpse of blockchain’s robust property rights management potential with NFTs or non-fungible tokens. These are unique tokens that can signal ownership over an item or asset. Imagine a future where you could acquire the rights to a piece of land digitally within a matter of minutes instead of days.
From decentralized finance to Web3, blockchain technology has found use-cases beyond simple payments.
Since the ownership record lives on a blockchain, nobody can dispute or tamper with it. The technology also simplifies aspects like fractional ownership and property transfers, both of which would involve a simple transaction. In contrast, equivalent paper-based processes are slow and corruption-prone, particularly when manual human input is involved.
Of course, all of this is still a bit of a fantasy — true real estate transactions on a blockchain won’t be commonplace for decades. Still, the technology’s robustness has already proven itself with platforms like Decentraland, where a virtual plot sold for nearly one million dollars.
Further reading: What is a crypto wallet and how does it work?