Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
Features
Just downloaded One UI 7? Here are two settings to change immediately
0

Features
Gemini’s vs ChatGPT’s Deep Research: For me, the choice is clear
0
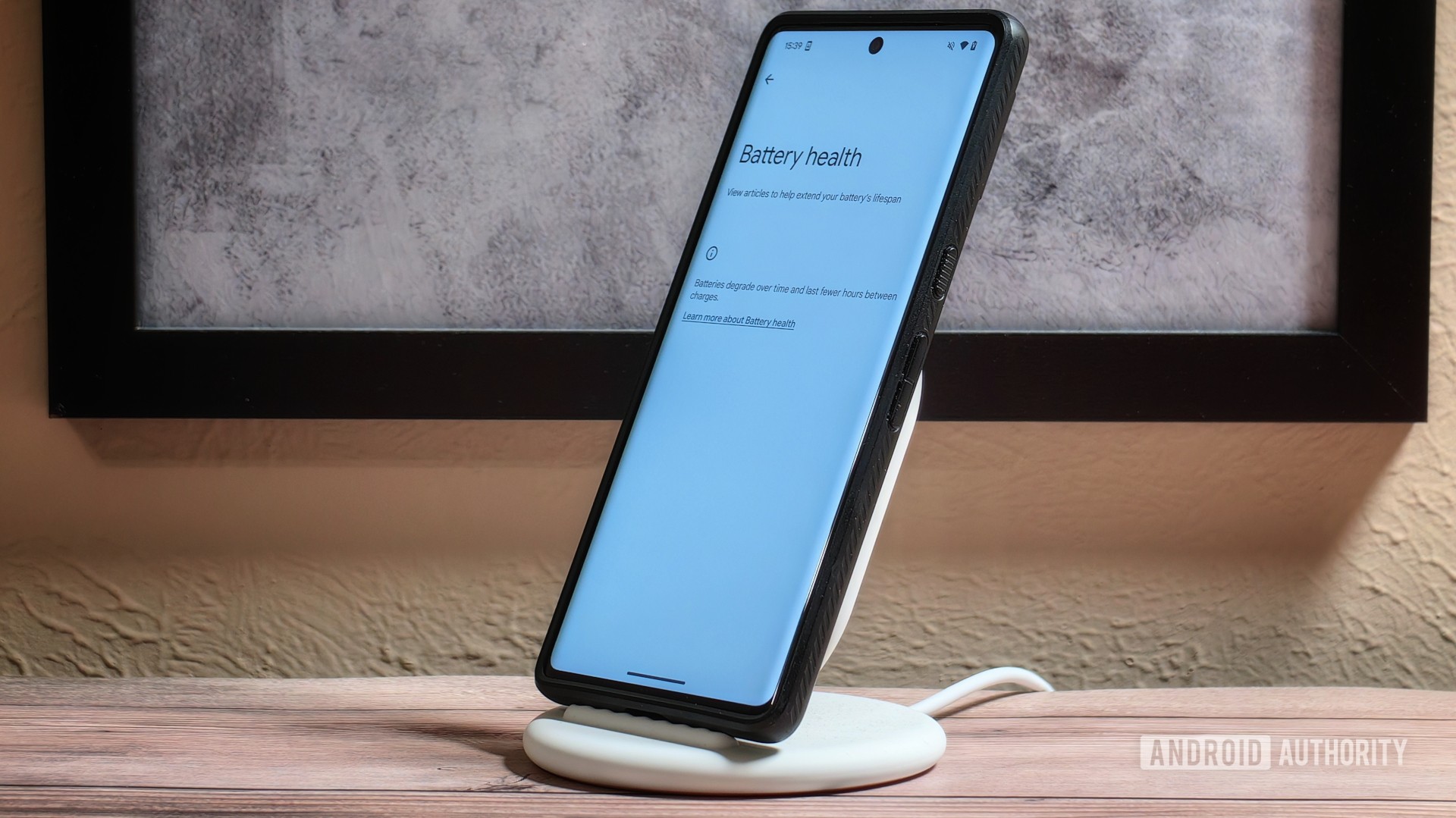
News
Google leaves older Pixels behind for Android’s long-awaited Battery Health menu
0
Latest poll
Would you rather buy the Pixel 8a or the Galaxy A35?
484 votes
In case you missed it
More news

Nick FernandezMay 6, 2025
0
Amazon Luna: Everything you need to know about Amazon's cloud gaming service
The best new Android apps and games for May 2025
Andy WalkerApril 30, 2025
0

These are my 10 favorite Android games to play with a controller
Nick FernandezApril 30, 2025
0

What happens to your data if you stop paying for Google One?
Mitja RutnikApril 28, 2025
0

Will Starlink and other satellite companies eventually rival cellular carriers?
Andrew GrushApril 26, 2025
0

A Pixel 8 was left in a hot tub for four days, here's what happened
Ryan McNeal13 hours ago
0

One UI 8 Watch is exploring half-size tiles, and here's what they look like
Aamir Siddiqui13 hours ago
0

How to enable Android 16's Audio Sharing feature on your Pixel
Mishaal Rahman15 hours ago
0

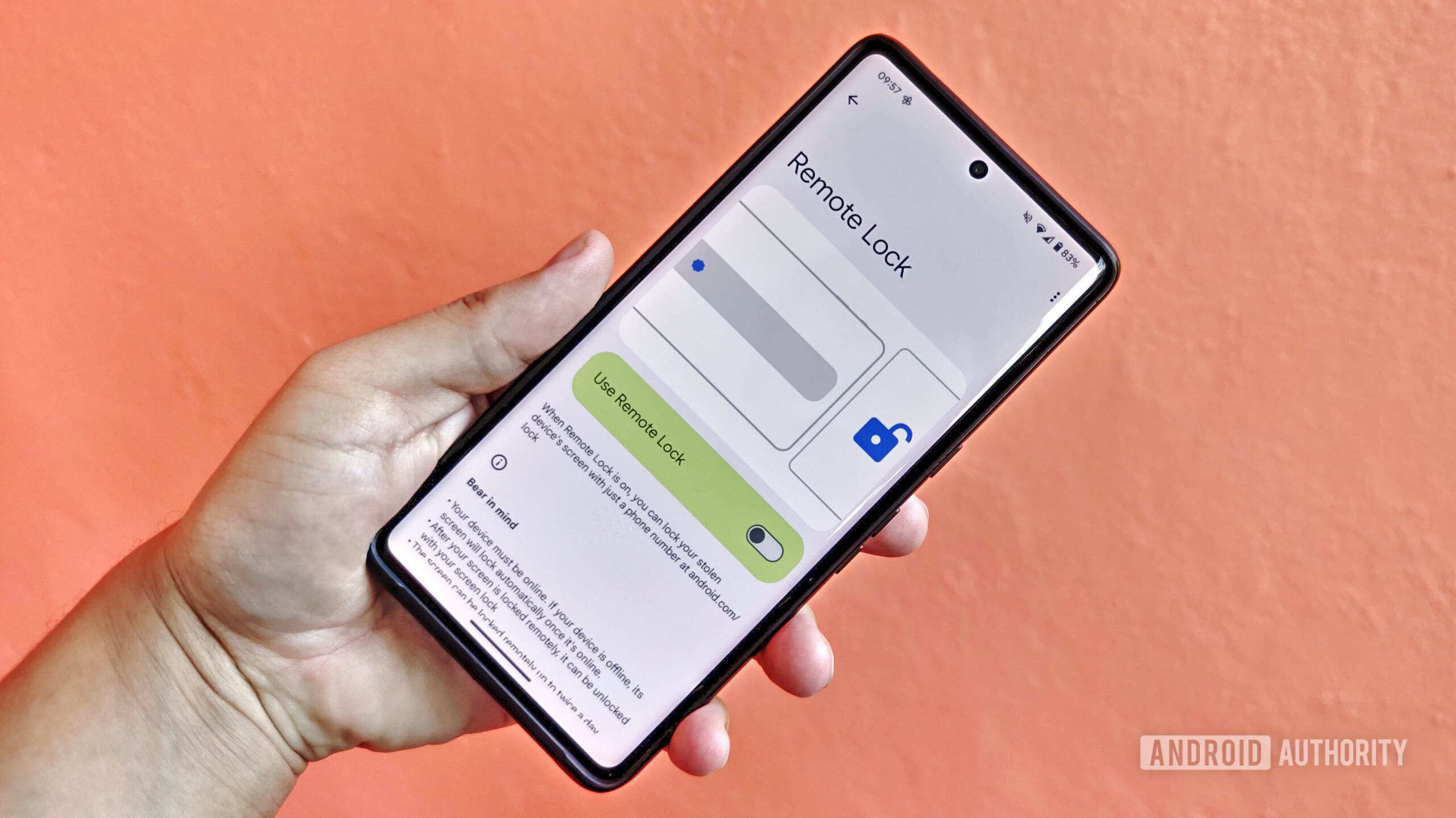
Remote Lock on Android isn't very secure, but a fix is coming (Update: Security questions)
Hadlee Simons17 hours ago
0
Miss the S23 Ultra's 10x camera? This brand could revive it (and then some)
Hadlee Simons17 hours ago
0

An exciting new Switch emulator launches tomorrow — Here's how to get it
Nick Fernandez19 hours ago
0

One UI 8 Watch isn't out yet, but here's its new One UI 7-like charging animation (APK teardown)
Hadlee Simons20 hours ago
0

Galaxy Watch 8 series could come with squircle design, Quick Button, and more (APK teardown)
Aamir Siddiqui20 hours ago
0

Google is bringing automatic passkey upgrades to Android (APK teardown)
Hadlee Simons21 hours ago
0
Samsung confirms brand-new Gorilla Glass display protection for Galaxy S25 Edge
Adamya Sharma24 hours ago
0