Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
What is PaLM 2: Google's large language model explained
Published onMarch 7, 2024

Even though Google was one of the first adopters of generative AI, it found itself blindsided by the explosive growth of rivals like ChatGPT and Microsoft Copilot. So in response, Google launched its Bard AI chatbot to mixed reception on March 21 2023. Eventually, it also added the ability to use Bard right from within Google’s search results. So in this article, let’s take a closer look at PaLM 2 and how it differs from previous Google models.
PaLM 2: Architecture and how does it work?
PaLM stands for Pathways Language Model, which signals the use of Google’s Pathways AI architecture that helps train machine learning models to perform a variety of tasks. It’s a big part of Google’s vision to reach general artificial intelligence or AGI.
Google previously stated the Pathways architecture will pave the way for multi-modal AI beyond text, something it’s since accomplished with the launch of Gemini. In a blog post, the company said,
Pathways could enable multimodal models that encompass vision, auditory, and language understanding simultaneously. So whether the model is processing the word “leopard,” the sound of someone saying “leopard,” or a video of a leopard running, the same response is activated internally: the concept of a leopard. The result is a model that’s more insightful and less prone to mistakes and biases.
While Google first spoke about PaLM in 2022, the company never launched a product utilizing it. However, with mounting pressure from the competition, Google eventually upgraded its Bard chatbot to use PaLM 2. Unlike the LaMDA model it replaces, PaLM 2 was trained on over 100 languages and has even better domain-related knowledge in areas like coding. It also has much better logical reasoning and mathematical capabilities.
From a technical perspective, Google’s first-generation LaMDA machine learning model boasted 137 billion parameters and a training size of 1.56 trillion words. This time around, Google says that PaLM 2 uses a new technique known as compute-optimal scaling to produce better results with fewer parameters and a smaller training dataset.
Google hasn’t committed to bringing multi-modal abilities to its AI products like Bard just yet. However, its future Gemini language model will likely bring support for images, audio, and more.
PaLM 2 vs. PaLM and LaMDA: How does Google’s latest LLM compare to predecessors?

PaLM 2’s capabilities previously gave Google Bard a pretty big boost in terms of capabilities. Google previously published a 92-page technical report detailing how PaLM 2 improves upon its predecessors, but let’s cut to the chase. Here’s a quick summary of the improvements over the company’s previous models:
- PaLM 2 was trained on a mix of languages and its training data included many non-English text samples. It also performs better at foreign language tests than LaMDA and first-gen PaLM.
- It sports better logical reasoning capabilities than its predecessors and even manages to match GPT-4 in the tests Google performed.
- Google’s Bard chatbot can now generate and debug code. That wasn’t possible with the company’s previous language models.
- PaLM 2 can translate between languages better than previous language models. In fact, it can also surpass Google Translate in certain languages like Portuguese and Chinese.
- With the new Pathways architecture, PaLM 2 is more efficient to train and use. This makes it more economical and feasible to include in Google services like Gmail.
- Google can fine-tune the PaLM 2 model for specific use cases. For example, Sec-PaLM is optimized to detect cybersecurity vulnerabilities, while Med-PaLM provides answers to medical queries.
Is Google PaLM 2 better than GPT-4?
OpenAI, the creator of ChatGPT, has so far managed to surpass other language models in terms of capabilities. But how does PaLM 2 compare? According to the company’s technical report, it scores better on common-sense tests. However, it falls behind in some other areas like its 8,000 token context window, which pales in comparison to GPT-4 Turbo’s 128,000 window.
That said, synthetic benchmarks don’t necessarily translate to real-world performance. So to find out which one came out ahead, I previously asked Google Bard and Bing Chat a couple of riddles. Microsoft uses OpenAI’s GPT-4 as the foundation for Bing Chat and I used a bit of creative prompt engineering to keep it from searching the internet for a response. Here’s the result of the first riddle I asked.
As you can see in the above screenshots, both Google Bard and GPT-4 managed to solve the riddle correctly. In fact, PaLM 2 also gave me an alternative solution that Bing Chat did not offer up. However, Google’s Bard chatbot refused to solve another riddle I threw at it. Bing Chat, meanwhile, gave in-depth detailed reasoning and the correct solution when asked the same riddle.
While these two examples don’t test PaLM 2’s full capabilities, they prove that Google has started to catch up with the competition but still has a fair bit of work left to do.
How does Google PaLM 2 compare to Gemini?
Google Gemini is a massive upgrade to PaLM 2. While PaLM 2 struggled to compete with GPT, Gemini is much more evenly matched on paper. Gemini is a multimodal LLM, meaning it offers different modes for specific use cases. You can learn more about the different versions of Gemini in our guide comparing Google Gemini Ultra vs Gemini Pro vs Gemini Nano.
How will Google use PaLM 2? Bard and developer APIs

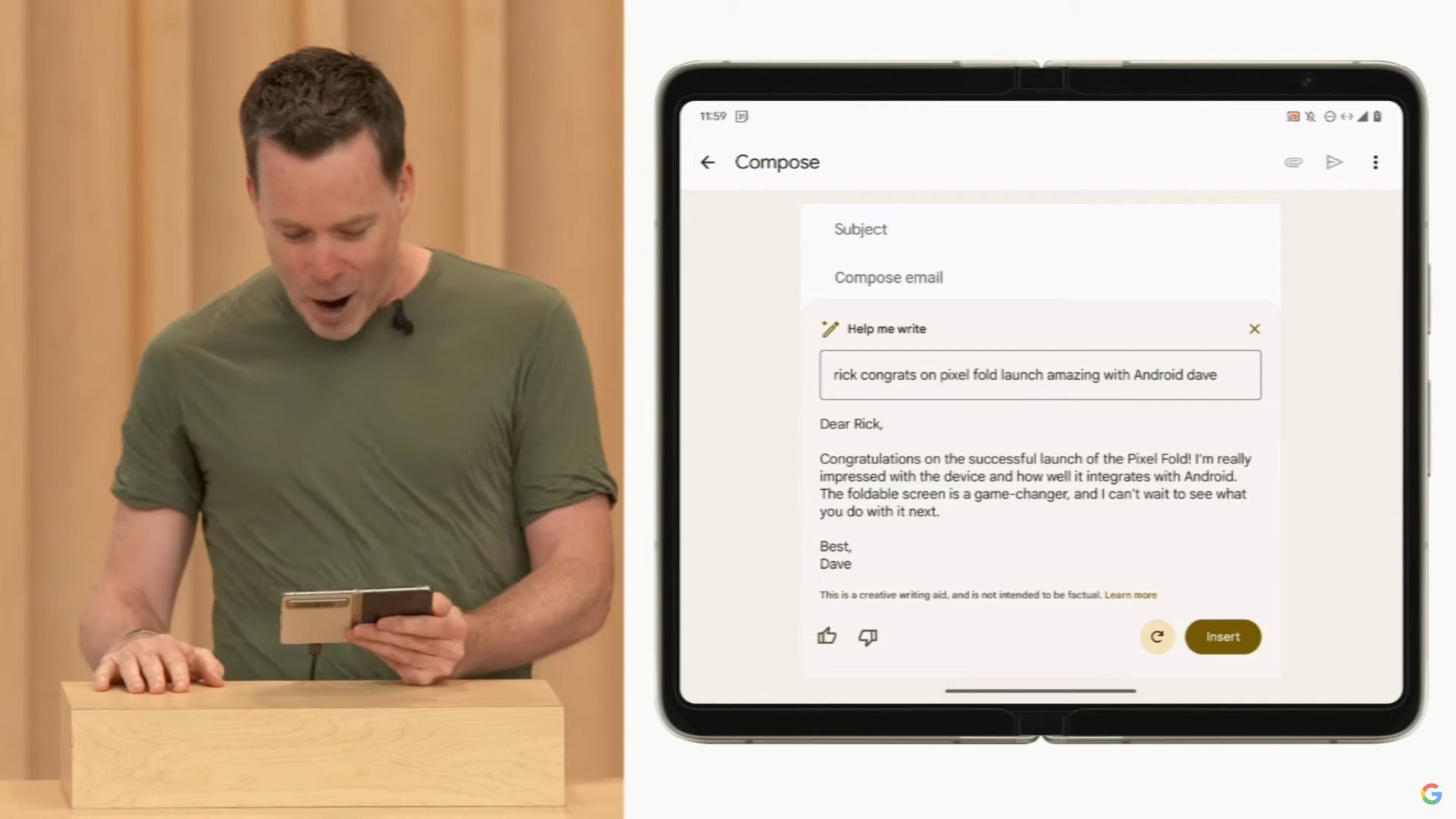
At Google’s I/O developer conference, we got a glimpse at the company’s plans for the future of PaLM 2 and its AI developments in general. The latest language model will power everything from a new “Help me Write” feature in Google Docs and Gmail to AI image generation in Slides. Broadly, these features fall under Google’s Duet AI for Workspace umbrella and we should see them roll out to the public in the coming months.
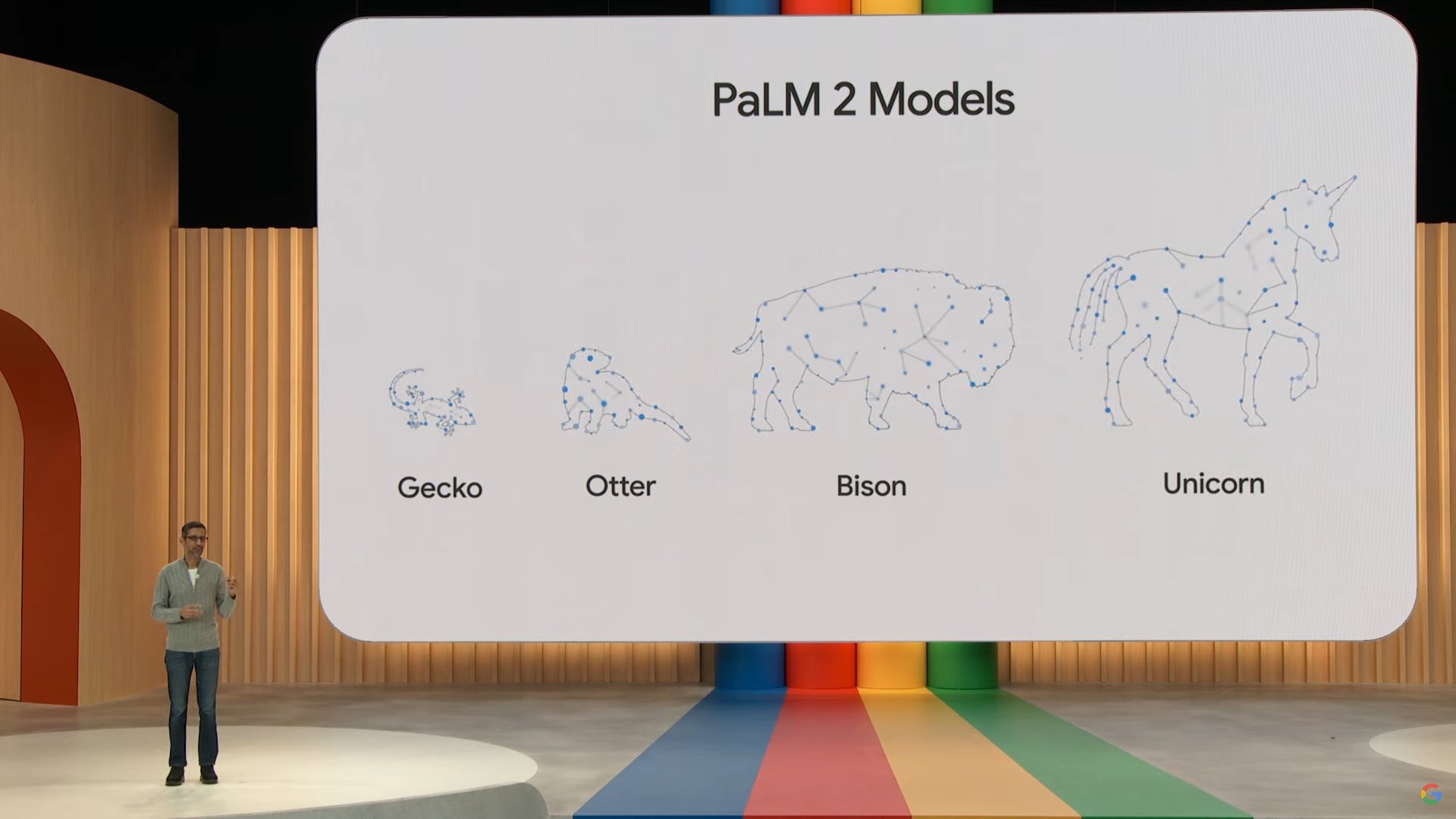
Google has also developed a version of PaLM 2 to fit on smartphones. Codenamed Gecko, this condensed language model could someday make it possible to use generative AI completely offline on a typical Android smartphone. We may see some generative AI features appear in future Pixel smartphones based on this information, but that’s purely speculation at this point.
Finally, software developers can now access PaLM 2 programmatically via APIs. This means we may see other companies rely on Google’s large language model, just like we’ve seen Duolingo and Khan Academy adopt GPT-4 for their respective AI-powered features. If you’re looking for a taste of PaLM 2 from a more casual perspective, however, I’d recommend talking to Google’s Bard chatbot.
FAQs
Google PaLM 2 is the large language model that powers Bard, the company’s AI chatbot, and other features like Help me Write in Gmail.
Google hasn’t released Med-PaLM 2 yet. The company will first grant access to a small group of trusted testers. It’s unclear if it will ever become publicly available.