Affiliate links on Android Authority may earn us a commission. Learn more.
What is a periscope camera lens, and how does it work?
Published onNovember 6, 2023

Phones have largely plateaued in performance, as even budget smartphones have what it takes to serve an average user. As a result, most of the tangible differentiation we see on high-end smartphones these days is on the camera. Camera flagship phones focus on quality and versatility, and one of the tools they have adopted for the latter is a periscope zoom lens. But what exactly is a periscope lens, and how does it help your phone camera zoom? We explore this in this article.
QUICK ANSWER
A periscope camera lens is a lens assembly that uses prisms, mirrors, or a combination of them to redirect light before it reaches the camera sensor. In doing so, it magnifies the image more so than it would have been possible in a regular lens or even telephoto lens assembly.
JUMP TO KEY SECTIONS
What is a periscope camera lens?

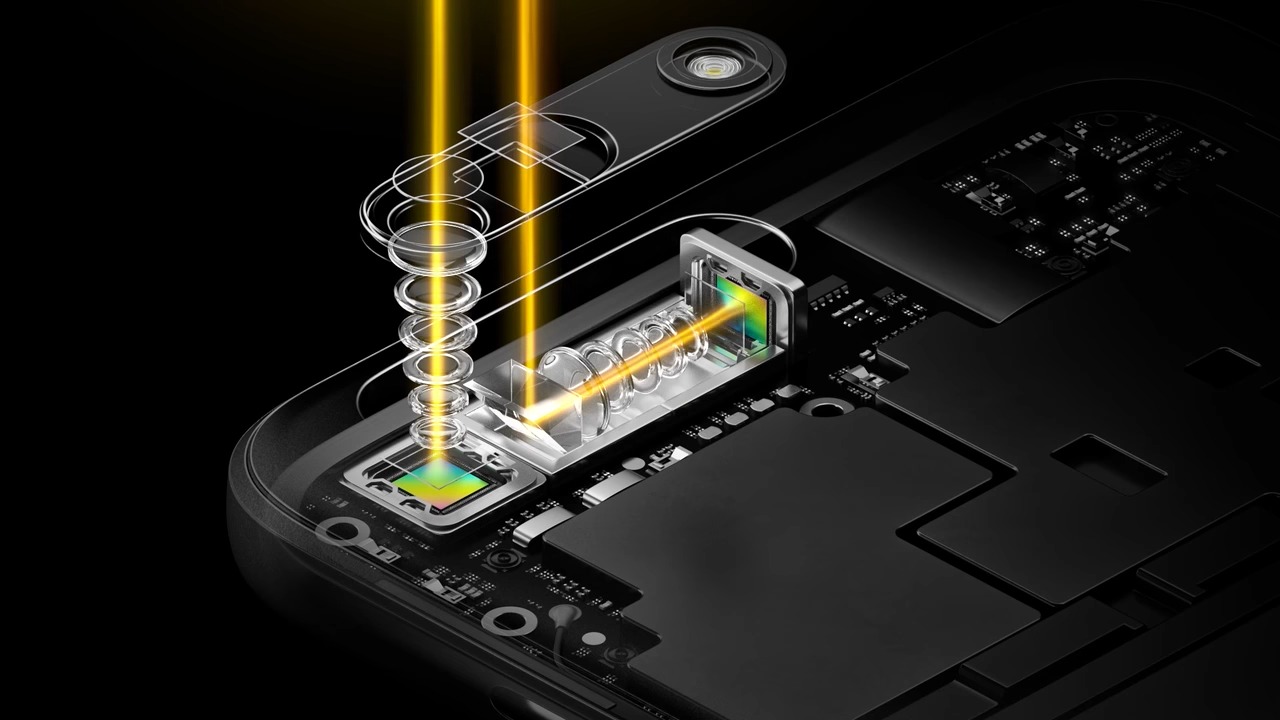
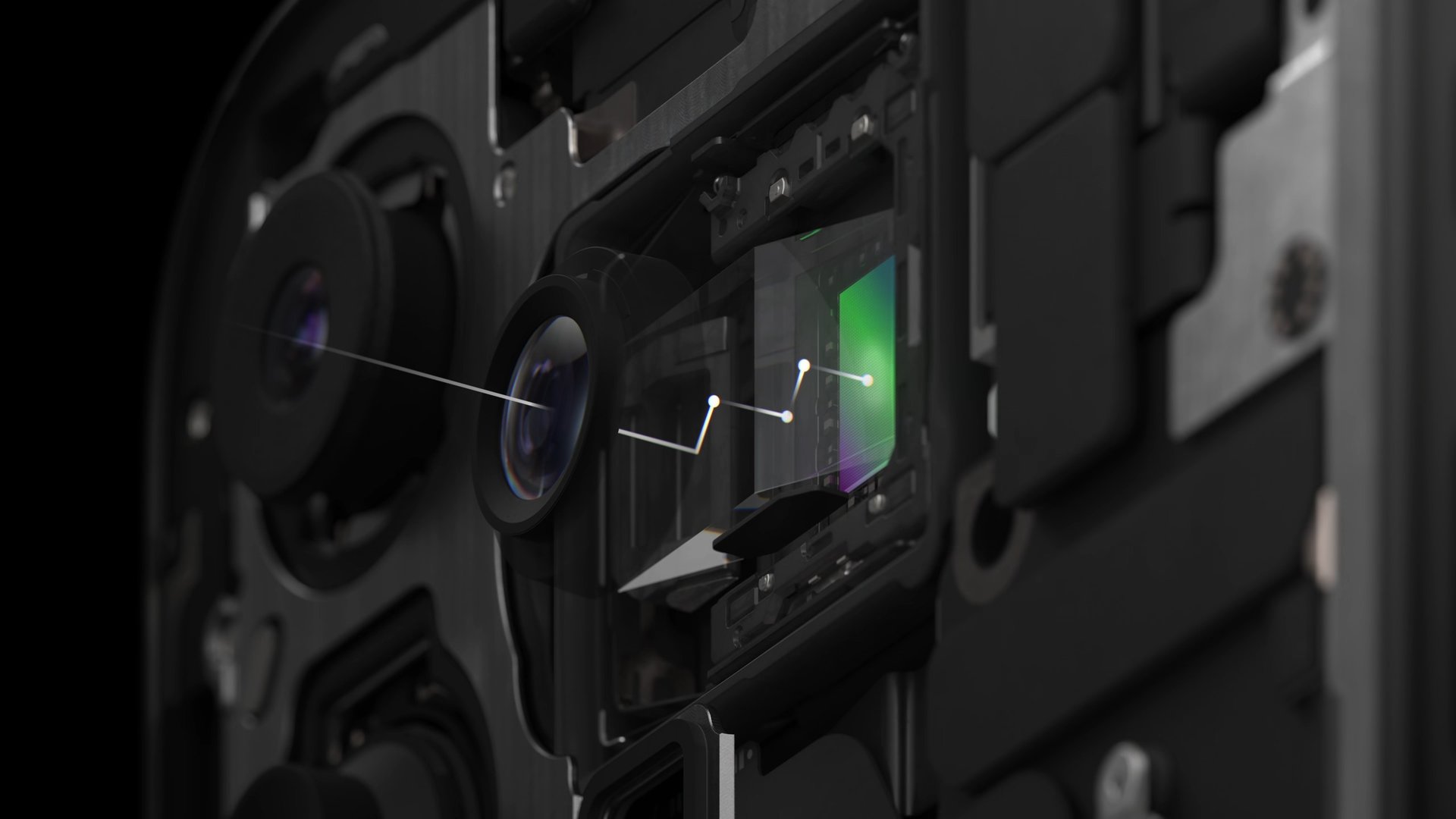
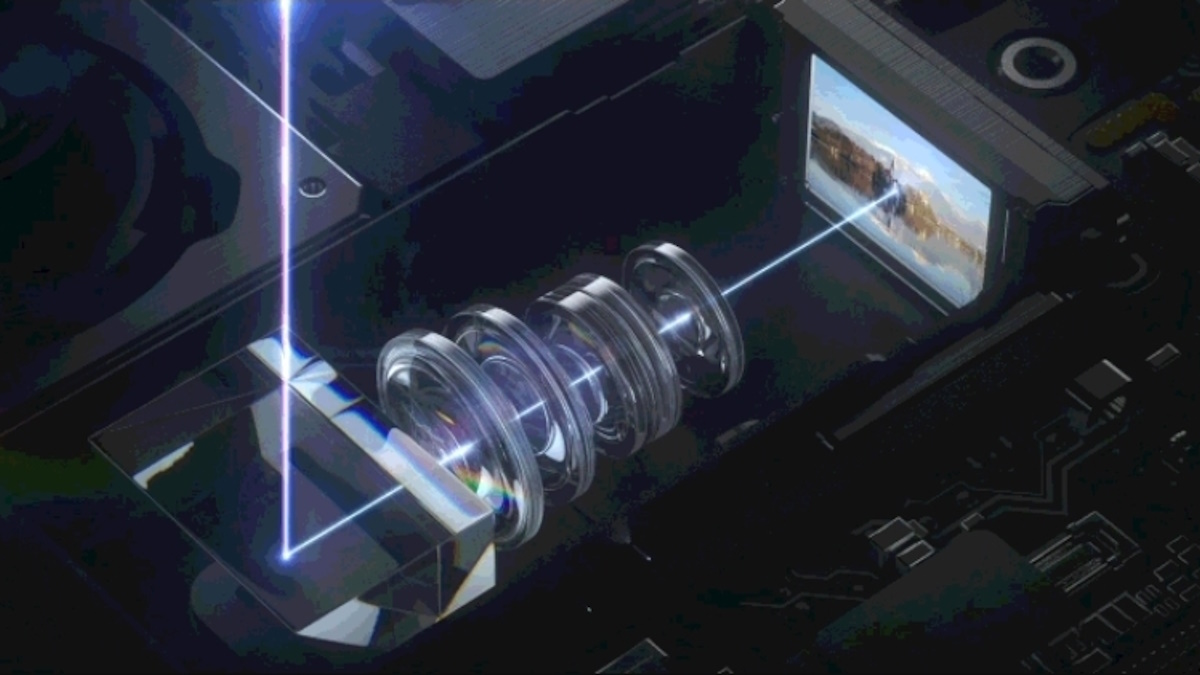
A periscope camera lens is a lens assembly that uses prisms or mirrors (or a combination of both) to refract, reflect, and redirect light before it reaches the camera sensor. There are magnification lenses built into this refraction and reflection path, allowing for optical magnification of the image more than what would have been otherwise possible in a conventional wide-angle lens assembly or telephoto lens assembly.
A periscope lens is called a “periscope” lens because the image sensor is placed perpendicular (and not parallel, as is with most other lenses) to the back of the phone.
Periscope lens is also called folded lens to reference the folded optics principles behind their functioning. A folded optic system refers to setups that send light on an optical trajectory longer than the size of the physical system. This is achieved by bouncing the light around.
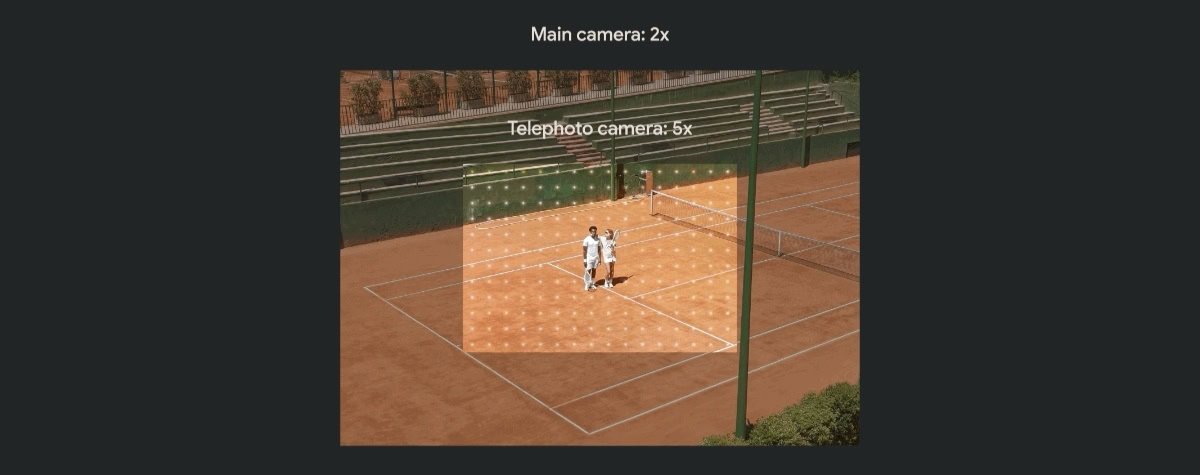
Periscope camera lenses are usually used to provide optical zoom ranging from 3x to as much as 10x, further opening up digital zoom (i.e., cropping) for up to 120x on certain smartphones. In contrast, a conventional telephoto camera sensor manages zoom, usually between 2x to 3.2x ranges, and some more through digital zoom and in-sensor zoom (using a high megapixel sensor and then cropping in).
Some smartphone companies use a combination of optical, digital, and in-sensor zoom across the primary sensor, telephoto sensor, and periscope zoom sensor to serve various zoom ranges.
How does a periscope camera lens work?

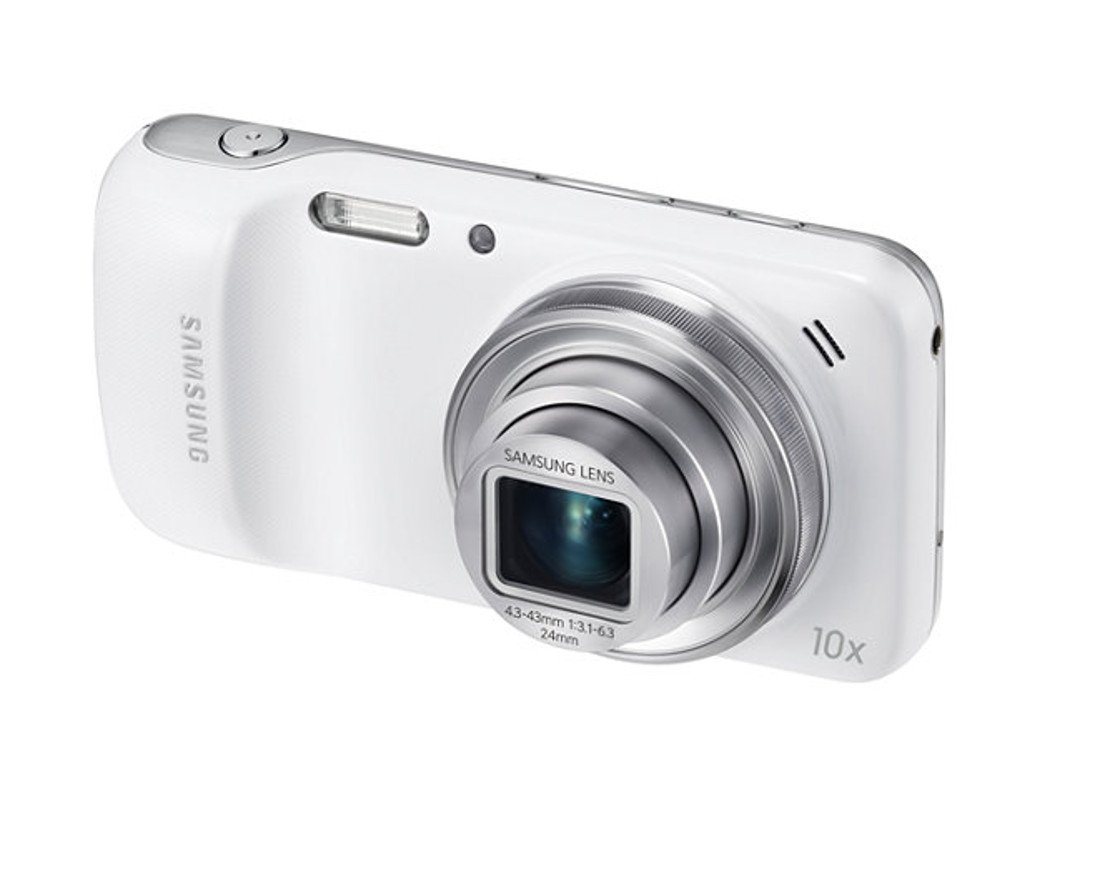
On dedicated cameras like DSLRs, optical zoom is achieved with the help of a protruding lens assembly. These lens assemblies usually have a lot of distance between the individual glass lenses inside, which is needed for the requisite magnification. Certain smartphones, like the Samsung Galaxy S4 Zoom, have used the same techniques to provide 10x optical zoom, but you can see how far ahead the camera setup needs to move to accommodate the required optical trajectory.

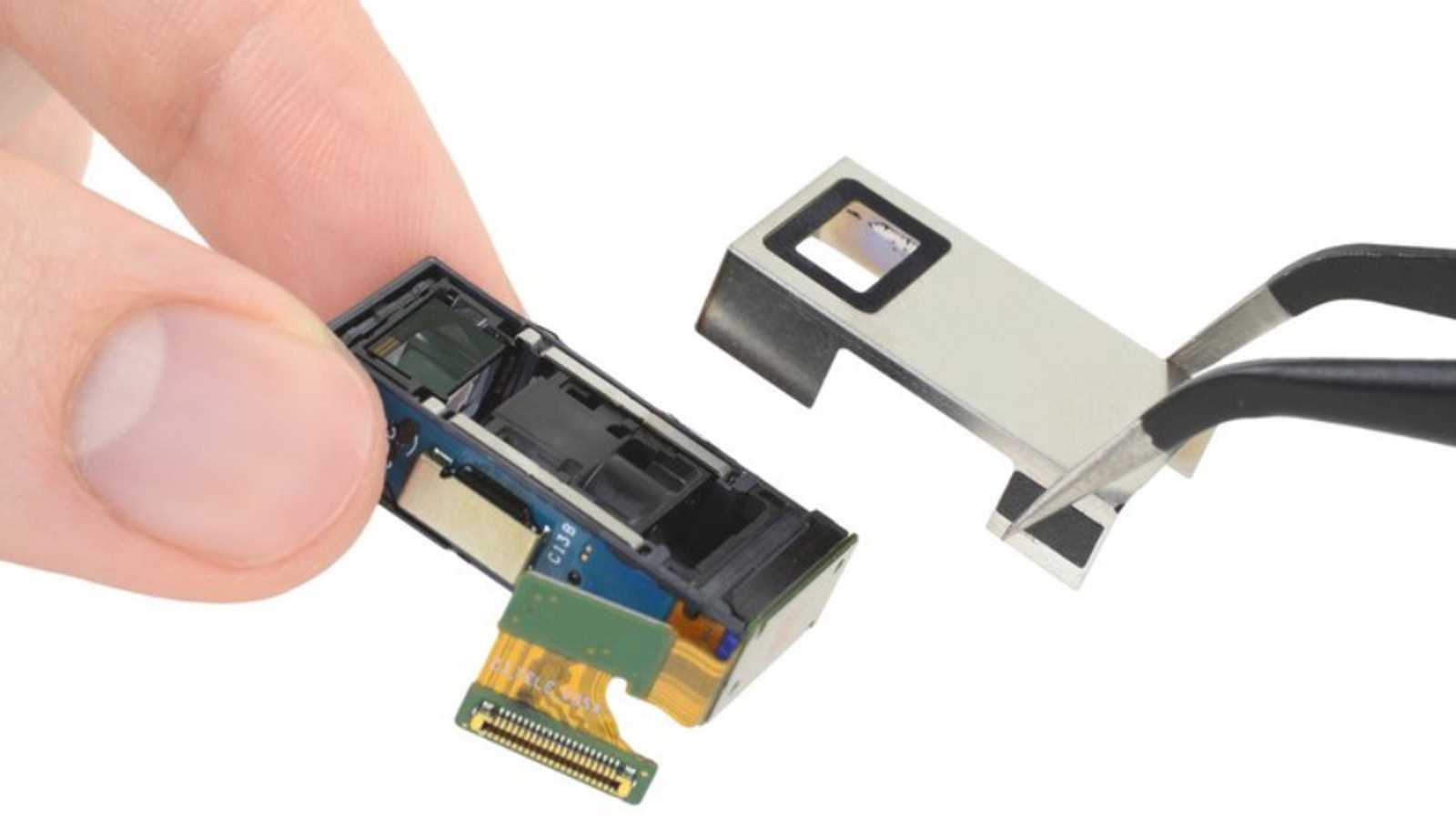
Modern-day smartphones don’t have the same luxury of space. Thus, periscope camera lenses are used to bounce around light for the needed magnification to occur in a smaller area. With clever angling of the image sensor, phones can fit a longer optical trajectory when using a periscope zoom setup.
A periscope camera lens setup broadly contains three main parts:
- A prism lens (or mirror on some phones) receives light from the outside, changes its direction by refraction or reflection, and redirects it to the inside of the assembly.
- Most periscope cameras will have a rectangular opening (as opposed to a circular opening for regular camera lenses) to let the prism do its work. This is the easiest way to recognize a periscope zoom camera.
- A series of concave and convex lenses that magnifies the light that is passing through.
- An image sensor that sits angled perpendicular to the body of the phone, receiving the magnified image.
Phone OEMs have been experimenting with cameras and periscope cameras. They have introduced concepts like auto-focus, OIS, sensor-shift OIS, in-sensor zoom, and more. You may find additional hardware on your flagship Android phone that helps add these features.
What is “tetraprism telephoto” on the iPhone 15 Pro Max?
Smartphones like the iPhone 15 Pro Max use a different lens setup, which Apple calls “tetraprism telephoto.” It uses the concept of periscope zoom lenses but skips out on the complex concave and convex lens assembly. Instead, it uses the prism to reflect light multiple times within a smaller footprint than conventional periscope zoom lenses.
What are the benefits of a periscope camera lens?
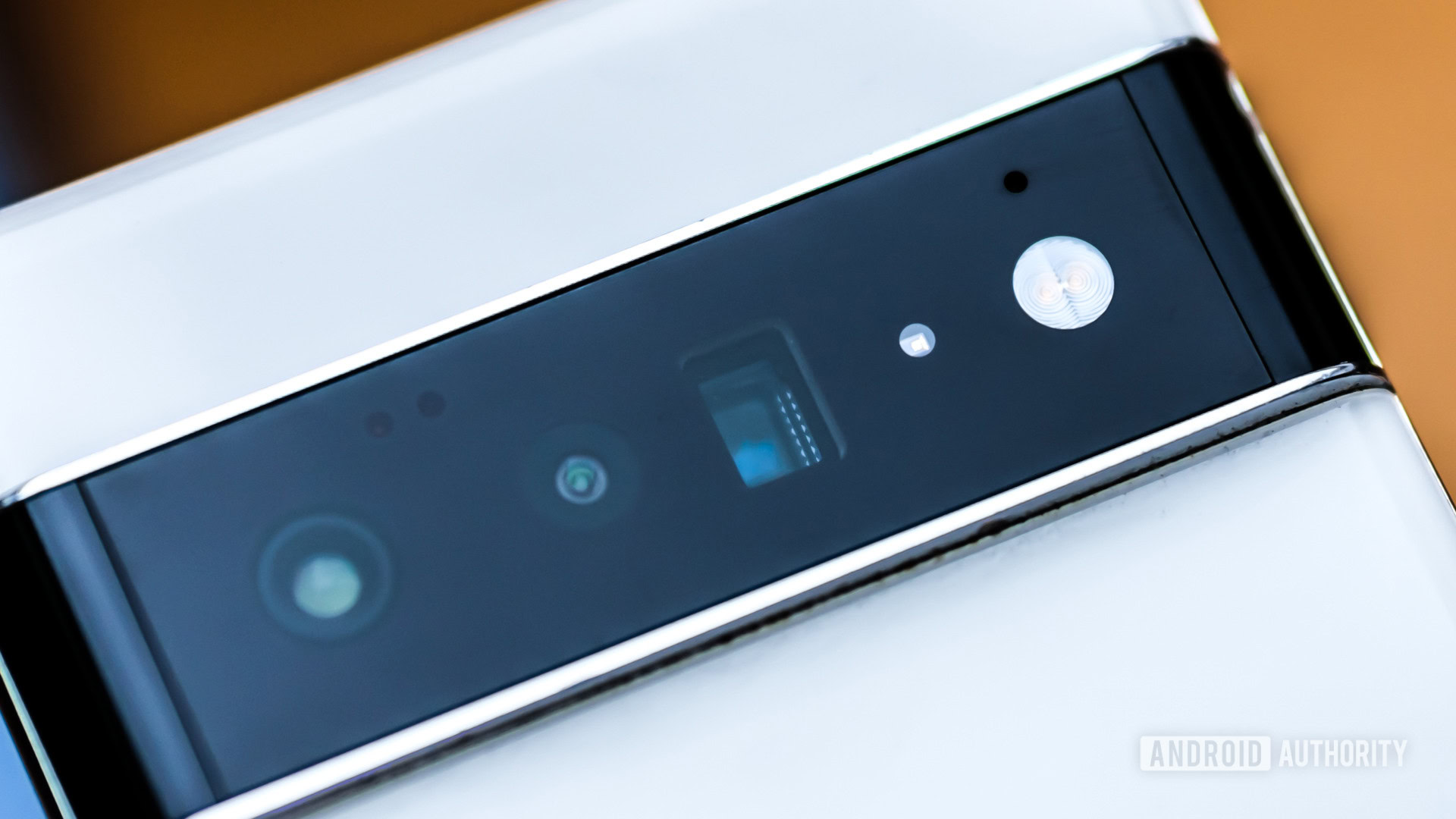

The biggest benefit to using a periscope camera lens is that it adds the ability to shoot subjects that are much farther away without a loss in quality. It opens up longer focal length ranges that are otherwise difficult to accommodate within a smartphone. You wouldn’t have been able to capture scenes that far away without making everything look like a fuzzy blob.
Image quality is the big win here. You can get really zoomed-in photos at good quality levels without resorting to digital zoom. The existence of a periscope camera lens adds to the versatility of the phone.
Periscope camera lenses also open up space inside the phone in a way. While they are large assemblies by themselves, the results that they achieve would have otherwise required an even bigger setup.
What are some drawbacks of a periscope camera lens?

Despite being compact for the results they achieve, periscope camera lens assemblies are large assemblies when contextualized against the size of your smartphone and its other components. Your phone has limited physical space, and a periscope zoom lens would occupy a big chunk of it. Even Apple’s tetraprism setup, which is more compact than periscope zoom lenses from other OEMs, is larger than the other sensors on the iPhone 15 Pro Max.
Periscope camera lenses also have a range of zoom that they can function the best in, and so they lack versatility to that extent. If you have a close-up subject, the assembly is wholly ineffective. As a result, a periscope camera lens needs to be accompanied by the usual standard camera lens and an optional telephoto camera lens, which can handle zoom duties between the standard camera and the periscope camera. For subjects further beyond the periscope zoom range, digital zoom would kick in, which doesn’t render good results beyond a point.
Since periscope cameras increase the focal length, the aperture also becomes narrower. This affects the amount of light that reaches the sensor. You’d either need to compensate by widening the aperture (which has its own drawbacks) or deal with mediocre results when the lighting isn’t perfect. Most phones end up with the latter due to space and cost constraints.
Periscope lens vs telephoto lens: How do they compare?

Periscope lenses and telephoto lenses both achieve optical zoom. How they go about it is where they differ.
In a telephoto lens, the magnification of the subject is achieved through a combination of convex and concave lenses. In its simplest form, a convex lens on the outside converges light. A conclave lens then diverges light back into parallel beams. A second convex lens can then be used to converge light once again onto the sensor. Modern telephoto lenses modify this basic assembly to provide optical zoom over short distances.
For telephoto zoom, you can expect to see anywhere between 2x to 3.2x zoom, depending on the complexity of the setup. The focal length is also preferred for portrait shots.
In contrast, a periscope zoom lens uses the periscope mechanism to achieve optical zoom. There may or may not be a convex-conclave lens assembly further within the periscope assembly. Depending on the complexity, you can get results between 3x to even 10x. This is more suitable for longer zoom needs.
Comparatively speaking, telephoto lens setups take up less space, have less complexity, and are usually cheaper. These reasons have made them popular in smartphones. Periscope zoom lenses take up more space, require rethinking the motherboard arrangement to accommodate an often perpendicular sensor, and cost more because of their complexity.
What are some phones with a periscope camera?
Periscope zoom lenses definitely have a place in the smartphone market, and we’re likely to see many premium smartphones take advantage of them. If you’re sold on the idea of a periscope zoom lens, here are some popular phones with a periscope zoom camera for you to choose from:
Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra
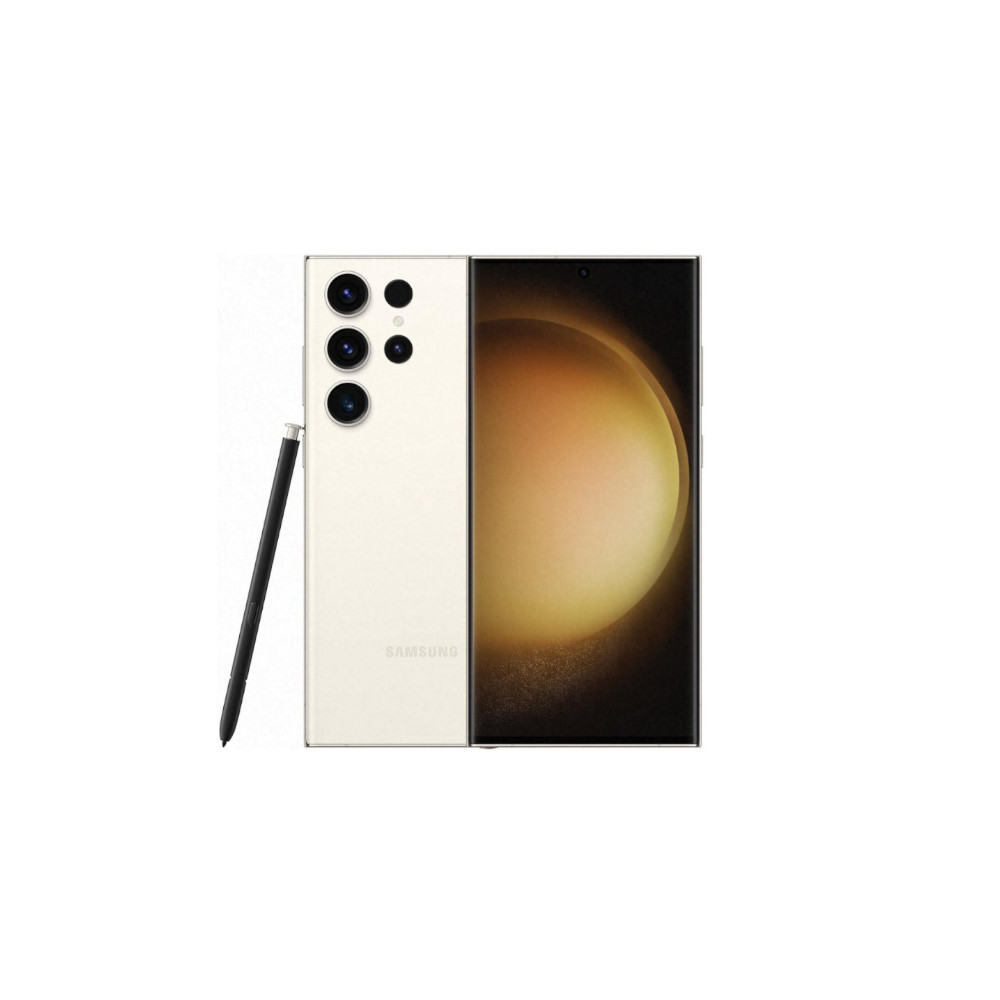


The Galaxy S23 Ultra is the most versatile camera smartphone around. It not only has a 10MP periscope zoom lens for 10x optical zoom, but it also complements it with a 10MP telephoto lens for 3x optical zoom.
Apple iPhone 15 Pro Max
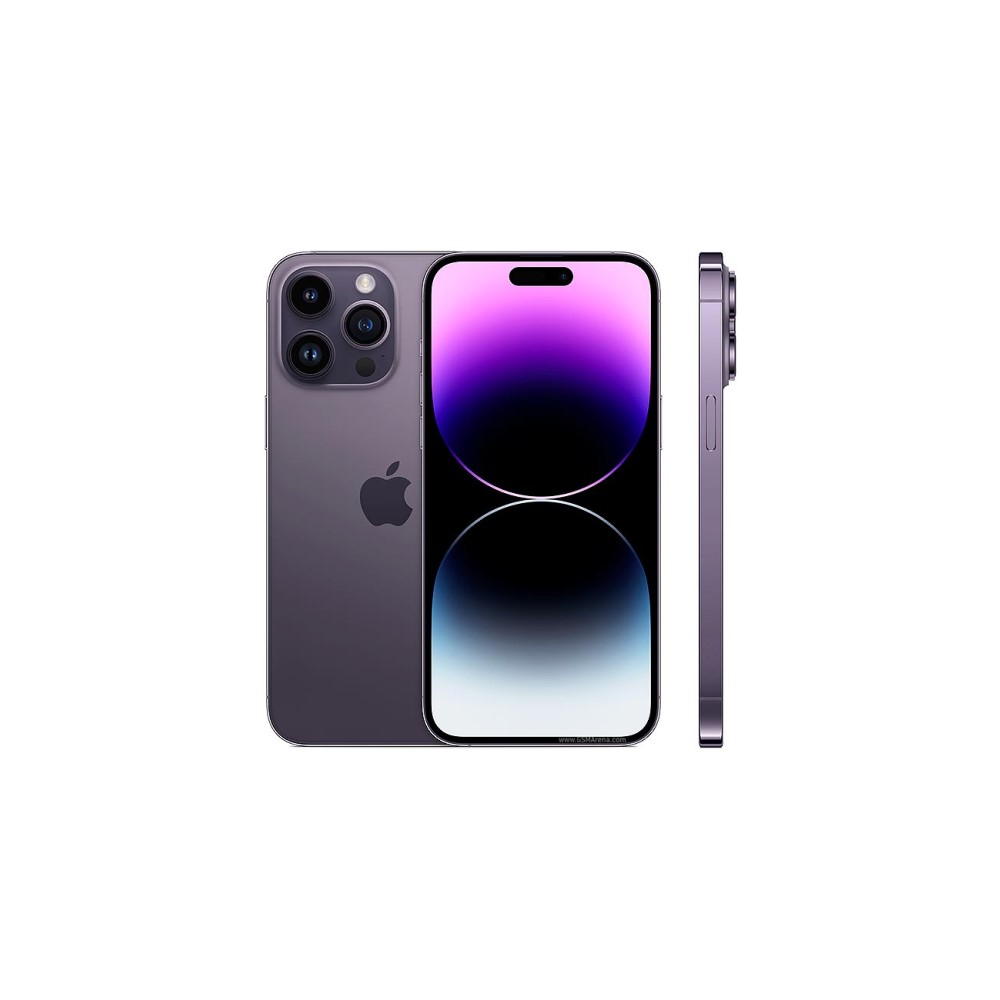

The iPhone 15 Pro Max is Apple’s first smartphone with a periscope zoom camera, namely the 12MP lens that can achieve 5x optical zoom. Apple calls it “tetraprism telephoto,” but the governing principles are similar.
Google Pixel 8 Pro
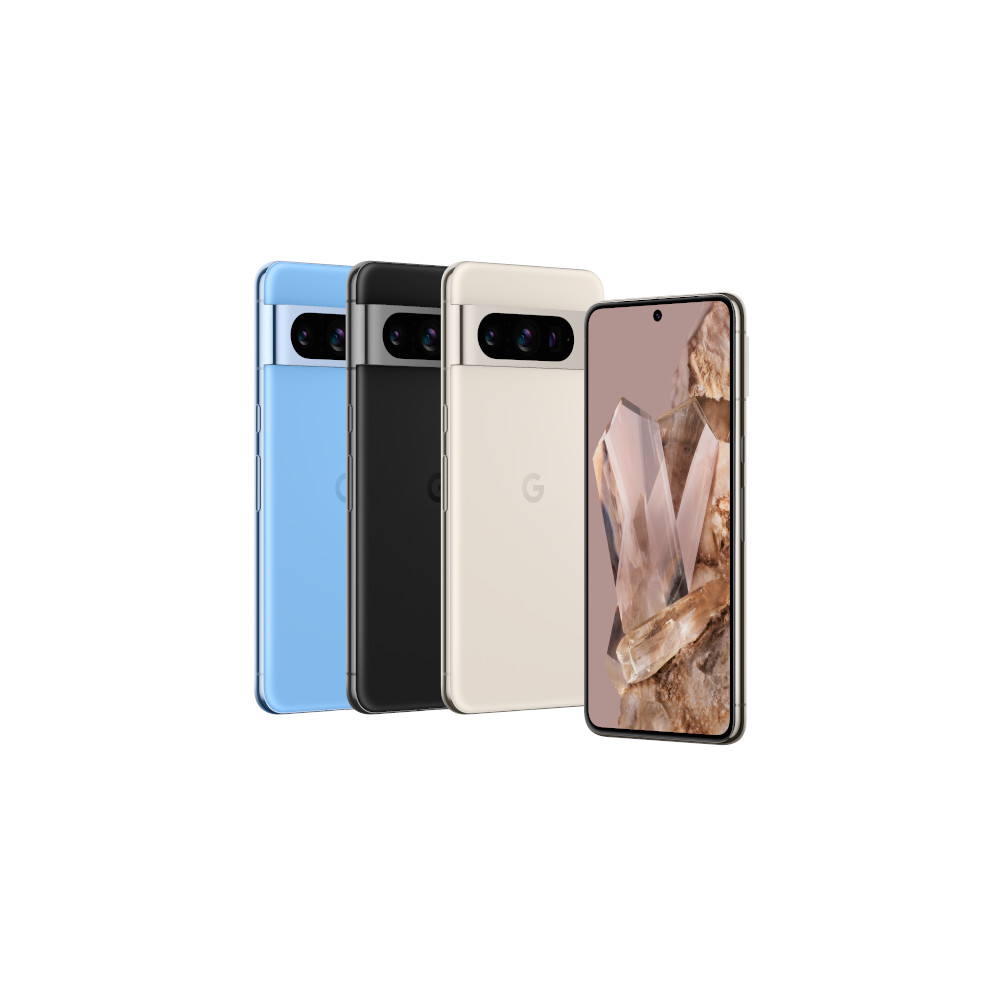


The Pixel 8 Pro also has a periscope zoom lens, coming in at 48MP for 5x optical zoom. Google leverages its AI smarts to fill in for versatility.
OnePlus Open


The OnePlus Open is a practical foldable with a 64MP periscope zoom camera, albeit at a modest 3x optical zoom. With the help of in-sensor zoom, you can get as much as 6x optical zoom.
FAQs
Yes. Generally speaking, a periscope lens is a very useful secondary lens on smartphones as it lets you shoot subjects at a further distance. A good periscope lens needs to be complemented with an excellent primary lens, though. This also adds cost and complexity to the smartphone, so the solution may not work out economically for budget and mid-range smartphones.